Interstellar is the first Hollywood movie to attempt depicting a black hole as it would actually be seen by somebody nearby. For this, our team at Double Negative Visual Effects, in collaboration with physicist Kip Thorne, developed a code called Double Negative Gravitational Renderer (DNGR) to solve the equations for ray-bundle (light-beam) propagation through the curved spacetime of a spinning (Kerr) black hole, and to render IMAX-quality, rapidly changing images. Our ray-bundle techniques were crucial for achieving IMAX-quality smoothness without flickering; and they differ from physicists' image-generation techniques (which generally rely on individual light rays rather than ray bundles), and also differ from techniques previously used in the film industry's CGI community. This paper has four purposes: (i) to describe DNGR for physicists and CGI practitioners, who may find interesting and useful some of our unconventional techniques. (ii) To present the equations we use, when the camera is in arbitrary motion at an arbitrary location near a Kerr black hole, for mapping light sources to camera images via elliptical ray bundles. (iii) To describe new insights, from DNGR, into gravitational lensing when the camera is near the spinning black hole, rather than far away as in almost all prior studies; we focus on the shapes, sizes and influence of caustics and critical curves, the creation and annihilation of stellar images, the pattern of multiple images, and the influence of almost-trapped light rays, and we find similar results to the more familiar case of a camera far from the hole. (iv) To describe how the images of the black hole Gargantua and its accretion disk, in the movie Interstellar, were generated with DNGR—including, especially, the influences of (a) colour changes due to doppler and gravitational frequency shifts, (b) intensity changes due to the frequency shifts, (c) simulated camera lens flare, and (d) decisions that the film makers made about these influences and about the Gargantua's spin, with the goal of producing images understandable for a mass audience. There are no new astrophysical insights in this accretion-disk section of the paper, but disk novices may find it pedagogically interesting, and movie buffs may find its discussions of Interstellar interesting.

Purpose-led Publishing is a coalition of three not-for-profit publishers in the field of physical sciences: AIP Publishing, the American Physical Society and IOP Publishing.
Together, as publishers that will always put purpose above profit, we have defined a set of industry standards that underpin high-quality, ethical scholarly communications.
We are proudly declaring that science is our only shareholder.
ISSN: 1361-6382
Classical and Quantum Gravity is an established journal for physicists, mathematicians and cosmologists in the fields of gravitation and the theory of spacetime. The journal is now the acknowledged world leader in classical relativity and all areas of quantum gravity.
Oliver James et al 2015 Class. Quantum Grav. 32 065001
Wolfgang Wieland 2025 Class. Quantum Grav. 42 06LT01
Recently, we introduced a non-perturbative quantization of impulsive gravitational null initial data. In this note, we investigate an immediate physical implication of the model. One of the quantum numbers is the total luminosity carried to infinity. We show that a transition happens when the luminosity reaches the Planck power  . Below
. Below 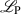 , the spectrum of the radiated power is discrete. Above the Planck power, the spectrum is continuous. A physical state that lies in the continuous spectrum consists of a superposition of kinematical states in which the shear is unbounded from above. We argue that such states are unphysical because they contain caustics that are in conflict with the falloff conditions at asymptotic infinity.
, the spectrum of the radiated power is discrete. Above the Planck power, the spectrum is continuous. A physical state that lies in the continuous spectrum consists of a superposition of kinematical states in which the shear is unbounded from above. We argue that such states are unphysical because they contain caustics that are in conflict with the falloff conditions at asymptotic infinity.
Germain Tobar and Fabio Costa 2020 Class. Quantum Grav. 37 205011
The theory of general relativity predicts the existence of closed time-like curves (CTCs), which theoretically would allow an observer to travel back in time and interact with their past self. This raises the question of whether this could create a grandfather paradox, in which the observer interacts in such a way to prevent their own time travel. Previous research has proposed a framework for deterministic, reversible, dynamics compatible with non-trivial time travel, where observers in distinct regions of spacetime can perform arbitrary local operations with no contradiction arising. However, only scenarios with up to three regions have been fully characterised, revealing only one type of process where the observers can verify to both be in the past and future of each other. Here we extend this characterisation to an arbitrary number of regions and find that there exist several inequivalent processes that can only arise due to non-trivial time travel. This supports the view that complex dynamics is possible in the presence of CTCs, compatible with free choice of local operations and free of inconsistencies.
L Gavassino 2025 Class. Quantum Grav. 42 015002
We study the internal dynamics of a hypothetical spaceship traveling on a close timelike curve in an axially symmetric Universe. We choose the curve so that the generator of evolution in proper time is the angular momentum. Using Wigner's theorem, we prove that the energy levels internal to the spaceship must undergo spontaneous discretization. The level separation turns out to be finely tuned so that, after completing a roundtrip of the curve, all systems are back to their initial state. This implies, for example, that the memories of an observer inside the spaceship are necessarily erased by the end of the journey. More in general, if there is an increase in entropy, a Poincaré cycle will eventually reverse it by the end of the loop, forcing entropy to decrease back to its initial value. We show that such decrease in entropy is in agreement with the eigenstate thermalization hypothesis. The non-existence of time-travel paradoxes follows as a rigorous corollary of our analysis.
Eleonora Di Valentino et al 2021 Class. Quantum Grav. 38 153001
The simplest ΛCDM model provides a good fit to a large span of cosmological data but harbors large areas of phenomenology and ignorance. With the improvement of the number and the accuracy of observations, discrepancies among key cosmological parameters of the model have emerged. The most statistically significant tension is the 4σ to 6σ disagreement between predictions of the Hubble constant, H0, made by the early time probes in concert with the 'vanilla' ΛCDM cosmological model, and a number of late time, model-independent determinations of H0 from local measurements of distances and redshifts. The high precision and consistency of the data at both ends present strong challenges to the possible solution space and demands a hypothesis with enough rigor to explain multiple observations—whether these invoke new physics, unexpected large-scale structures or multiple, unrelated errors. A thorough review of the problem including a discussion of recent Hubble constant estimates and a summary of the proposed theoretical solutions is presented here. We include more than 1000 references, indicating that the interest in this area has grown considerably just during the last few years. We classify the many proposals to resolve the tension in these categories: early dark energy, late dark energy, dark energy models with 6 degrees of freedom and their extensions, models with extra relativistic degrees of freedom, models with extra interactions, unified cosmologies, modified gravity, inflationary models, modified recombination history, physics of the critical phenomena, and alternative proposals. Some are formally successful, improving the fit to the data in light of their additional degrees of freedom, restoring agreement within 1–2σ between Planck 2018, using the cosmic microwave background power spectra data, baryon acoustic oscillations, Pantheon SN data, and R20, the latest SH0ES Team Riess, et al (2021 Astrophys. J.908 L6) measurement of the Hubble constant (H0 = 73.2 ± 1.3 km s−1 Mpc−1 at 68% confidence level). However, there are many more unsuccessful models which leave the discrepancy well above the 3σ disagreement level. In many cases, reduced tension comes not simply from a change in the value of H0 but also due to an increase in its uncertainty due to degeneracy with additional physics, complicating the picture and pointing to the need for additional probes. While no specific proposal makes a strong case for being highly likely or far better than all others, solutions involving early or dynamical dark energy, neutrino interactions, interacting cosmologies, primordial magnetic fields, and modified gravity provide the best options until a better alternative comes along.
Germain Tobar et al 2025 Class. Quantum Grav. 42 055017
We propose a multi-mode bar consisting of mass elements of decreasing size for the implementation of a gravitational version of the photo-electric effect through the stimulated absorption of up to kHz gravitons from a binary neutron star merger and post-merger. We find that the multi-mode detector has normal modes that retain the coupling strength to the gravitational wave of the largest mass-element, while only having an effective mass comparable to the mass of the smallest element. This allows the normal modes to have graviton absorption rates due to the tonne-scale largest mass, while the single graviton absorption process in the normal mode could be resolved through energy measurements of a mass-element in-principle smaller than pico-gram scale. We argue the feasibility of directly counting gravito-phonons in the bar through energy measurements of the end mass. This improves the transduction of the single-graviton signal, enhancing the feasibility of detecting single gravitons.
B P Abbott et al 2020 Class. Quantum Grav. 37 055002
The LIGO Scientific Collaboration and the Virgo Collaboration have cataloged eleven confidently detected gravitational-wave events during the first two observing runs of the advanced detector era. All eleven events were consistent with being from well-modeled mergers between compact stellar-mass objects: black holes or neutron stars. The data around the time of each of these events have been made publicly available through the gravitational-wave open science center. The entirety of the gravitational-wave strain data from the first and second observing runs have also now been made publicly available. There is considerable interest among the broad scientific community in understanding the data and methods used in the analyses. In this paper, we provide an overview of the detector noise properties and the data analysis techniques used to detect gravitational-wave signals and infer the source properties. We describe some of the checks that are performed to validate the analyses and results from the observations of gravitational-wave events. We also address concerns that have been raised about various properties of LIGO–Virgo detector noise and the correctness of our analyses as applied to the resulting data.
Eleonora Castelli et al 2025 Class. Quantum Grav. 42 065018
The Laser Interferometer Space Antenna (LISA) mission is being developed by ESA with NASA participation. As it has recently passed the Mission Adoption milestone, models of the instruments and noise performance are becoming more detailed, and likewise prototype data analyses must as well. Assumptions such as Gaussianity, stationarity, and data continuity are unrealistic, and must be replaced with physically motivated data simulations, and data analysis methods adapted to accommodate such likely imperfections. To this end, the LISA Data Challenges have produced datasets featuring time-varying and unequal constellation armlength, and measurement artifacts including data interruptions and instrumental transients. In this work, we assess the impact of these data artifacts on the inference of galactic binary and massive black hole properties. Our analysis shows that the treatment of noise transients and gaps is necessary for effective parameter estimation, as they substantially corrupt the analysis if unmitigated. We find that straightforward mitigation techniques can significantly if imperfectly suppress artifacts. For the Galactic Binaries, mitigation of glitches was essentially total, while mitigations of the data gaps increased parameter uncertainty by approximately 10%. For the massive black hole binaries the particularly pernicious glitches resulted in a 30% uncertainty increase after mitigations, while the data gaps can increase parameter uncertainty by up to several times. Critically, this underlines the importance of early detection of transient gravitational waves to ensure they are protected from planned data interruptions.
Arnold Tianyi Yang et al 2025 Class. Quantum Grav. 42 065024
Spurious solar-wind effects are a potential noise source in future Laser Interferometer Space Antenna (LISA) measurements. One noise coupling mechanism is constrained by estimating solar-wind effects on acceleration noise in LISA Pathfinder (LPF). While LISA is designed for drag-free differential measurement, predicting the realistic impact both bounds the operational environment and assesses whether LISA could provide serendipitous space-weather observations. Data from NASA's Advanced Composition Explorer (ACE), situated at the L1 Lagrange point, serves as a reliable source of solar-wind data. The data sets are compared over the 114 d time period from 1 March 2016 to 23 June 2016. This period gives the longest readily-available open data set, without interference from other commissioning activities. To evaluate space weather effects, the data from both satellites are formatted, gap-filled/interpolated, and fast-Fourier transformed for amplitude spectral density and coherence comparisons. Solar wind effects are not seen in a coherence plot between LPF and ACE; modest coherence in the planned LISA observational frequency band can be attributed to chance. This result indicates that measurable correlation due to solar-wind acceleration noise over 3 month timescales will be a negligible noise source. LISA is unlikely to inform solar wind measurements routinely. Another source of noise from the Sun, solar radiation pressure, is estimated to impart greater acceleration noise, but has yet to be analyzed.
Luc Blanchet et al 2025 Class. Quantum Grav. 42 065015
We compute the gravitational radiation–reaction (RR) force on a compact binary source at the fourth-and-a-half post-Newtonian (4.5PN) order of general relativity, i.e. 2PN order beyond the leading 2.5PN radiation reaction. The calculation is valid for general orbits in a general frame, but in a particular coordinate system which is an extension of the Burke–Thorne coordinate system at the lowest order. With the RR acceleration, we derive (from first principles) the flux-balance laws associated with the energy, the angular and linear momenta, and the center-of-mass (CM) position, in a general frame and up to 4.5PN order. Restricting our attention to the frame of the center of mass, we point out that the equations of motion (EOM) acquire a non-local-in-time contribution at the 4.5PN order, made of the integrated flux of linear momentum (responsible for the recoil of the source) together with the instantaneous flux of CM position. The non-local contribution was overlooked in the past literature, which assumed locality of the RR force in the center of mass frame at 4.5PN order. We discuss the consequences of this non-local effect and obtain consistent non-local EOM and flux balance laws at 4.5PN order in the CM frame.
Simon Langenscheidt and Daniele Oriti 2025 Class. Quantum Grav. 42 075010
We present a set of noncommuting tetrad-shift symmetries in 4D gravity in tetrad-connection variables, which allow expressing diffeomorphisms as composite transformations. Working on the phase space level for finite regions, we pay close attention to the corner piece of the generators, discuss various possible charge brackets, relative definitions of the charges, coupling to spinors and relations to other charges. What emerges is a picture of the symmetries and edge modes of gravity that bears local resemblance to a Poincare group  , but possesses structure functions. In particular, we argue that the symmetries and charges presented here are more amenable to discretisation, and sketch a strategy for this charge algebra, geared toward quantum gravity applications.
, but possesses structure functions. In particular, we argue that the symmetries and charges presented here are more amenable to discretisation, and sketch a strategy for this charge algebra, geared toward quantum gravity applications.
Jeremy G Baier et al 2025 Class. Quantum Grav. 42 075008
As pulsar timing arrays (PTAs) transition into the detection era of the stochastic gravitational wave background (GWB), it is important for PTA collaborations to review and possibly revise their observing campaigns. The detection of a 'single source' would be a boon for gravitational astrophysics, as such a source would emit gravitational waves for millions of years in the PTA frequency band. Here we present generic methods for studying the effects of various observational strategies, taking advantage of detector sensitivity curves, i.e. noise-averaged, frequency-domain detection statistics. The statistical basis for these methods is presented along with myriad examples of how to tune a detector towards single, deterministic signals or a stochastic background. We demonstrate that trading observations of the worst pulsars for high cadence campaigns on the best pulsars increases sensitivity to single sources at high frequencies while hedging losses in GWB and single source sensitivity at low frequencies. We also find that sky-targeted observing campaigns yield minimal sensitivity improvements compared with other PTA tuning options. Lastly, we show the importance of the uncorrelated half of the GWB, i.e. the pulsar-term, as an increasingly prominent sources of noise and show the impact of this emerging noise source on various PTA configurations.
Richard Lieu 2025 Class. Quantum Grav. 42 07LT01
A set of temporal singularities (transients) in the mass-energy density and pressure, bearing a specific mathematical structure which represents a new solution to the continuity equation (i.e. conservation of mass-energy) and satisfying the strong energy condition, is proposed to account for the expansion history of a homogeneous Universe, and the formation and binding of large scale structures as a continuum approximation of their cumulative effects. These singularities are unobservable because they occur rarely in time and are unresolvably fast, and that could be the reason why dark matter and dark energy have not been found. Implication on inflationary cosmology is discussed. The origin of these temporal singularities is unknown, safe to say that the same is true of the moment of the Big Bang itself. This work complements a recent paper, where a topological defect in the form of a spatial, spherical shell of density singularity giving rise to a 1/r attractive force (to test particles of positive mass) but zero integrated mass over a large volume of space, was proposed to solve the dark matter problem in bound structures but not cosmic expansion. The idea also involved a negative density, which is not present in the current model.
Peng Qiu et al 2025 Class. Quantum Grav. 42 075009
Tilt-to-length (TTL) noise, caused by angular jitter and misalignment, is a major noise source in the inter-satellite interferometer for gravitational wave detection. However, the required level of axis alignment of the optical components is beyond the current state of the art. A set of optical parallel plates, called beam alignment mechanism (BAM), is proposed by LISA to compensate for the alignment error. In this paper, we show a prototype design of the BAM and demonstrate its performance in a ground-based optical system. We derive the BAM theoretical model, which agrees well with the numerical simulation. Experimental results reveal that the BAM can achieve lateral displacement compensation of the optical axis with a resolution of 1 µm across a range of about 0.5 mm. Furthermore, the TTL coefficient is reduced from about 0.3 mm rad−1 to about 5 µm rad−1, satisfying the preliminary requirements for LISA and TianQin. These findings confirm the efficacy of the BAM in suppressing TTL noise, offering a promising solution for space-based gravitational wave detection.
Sanjeev Kumar et al 2025 Class. Quantum Grav. 42 077001
We study the boson star solutions in a theory involving a complex scalar field in a conical scalar field potential:  in the presence of non-minimal gravity given by the term:
in the presence of non-minimal gravity given by the term:  in the action, where ξ is a constant parameter that couples the complex scalar field Φ with the Ricci scalar R and is treated, in our work, as a free parameter. The theory has one more free parameter denoted by
in the action, where ξ is a constant parameter that couples the complex scalar field Φ with the Ricci scalar R and is treated, in our work, as a free parameter. The theory has one more free parameter denoted by  (where ω is the frequency of the complex scalar field). Here G is the Newton's gravitational constant, λ is a constant used in the definition of the scalar field potential. We find that the acceptable boson star solutions exist in this theory that involves non-minimal gravity as above. For obtaining the acceptable boson star solutions, we obtain the domain of existence of our free parameters ξ and α for which the boson star solutions exist and then study the various properties of the boson star solutions. In our studies, as we trace the evolution of our solutions along the relevant path, emanating from the solutions corresponding to the absence of gravitational field, we observe a steady increase in mass with radius. Employing principles from catastrophe theory, we find that this trajectory remains stable until it reaches the maximum mass value. This leads to the characteristic spiraling behavior of the mass-radius curve, a well-known feature in compact star models signaling the onset of instability.
(where ω is the frequency of the complex scalar field). Here G is the Newton's gravitational constant, λ is a constant used in the definition of the scalar field potential. We find that the acceptable boson star solutions exist in this theory that involves non-minimal gravity as above. For obtaining the acceptable boson star solutions, we obtain the domain of existence of our free parameters ξ and α for which the boson star solutions exist and then study the various properties of the boson star solutions. In our studies, as we trace the evolution of our solutions along the relevant path, emanating from the solutions corresponding to the absence of gravitational field, we observe a steady increase in mass with radius. Employing principles from catastrophe theory, we find that this trajectory remains stable until it reaches the maximum mass value. This leads to the characteristic spiraling behavior of the mass-radius curve, a well-known feature in compact star models signaling the onset of instability.
R Alves Batista et al 2025 Class. Quantum Grav. 42 032001
The unification of quantum mechanics and general relativity has long been elusive. Only recently have empirical predictions of various possible theories of quantum gravity been put to test, where a clear signal of quantum properties of gravity is still missing. The dawn of multi-messenger high-energy astrophysics has been tremendously beneficial, as it allows us to study particles with much higher energies and travelling much longer distances than possible in terrestrial experiments, but more progress is needed on several fronts. A thorough appraisal of current strategies and experimental frameworks, regarding quantum gravity phenomenology, is provided here. Our aim is twofold: a description of tentative multimessenger explorations, plus a focus on future detection experiments. As the outlook of the network of researchers that formed through the COST Action CA18108 'Quantum gravity phenomenology in the multi-messenger approach (QG-MM)', in this work we give an overview of the desiderata that future theoretical frameworks, observational facilities, and data-sharing policies should satisfy in order to advance the cause of quantum gravity phenomenology.
D I Jones and K Riles 2025 Class. Quantum Grav. 42 033001
Rotating and oscillating neutron stars can give rise to long-lived Continuous Gravitational Waves (CGWs). Despite many years of searching, the detection of such a CGW signal remains elusive. In this article we describe the main astrophysical uncertainties regarding such emission, and their relation to the behaviour of matter at extremely high density. We describe the main challenges in searching for CGWs, and the prospects of detecting them using third-generation gravitational wave detectors. We end by describing some pressing issues in the field, whose resolution would help turn the detection and exploitation of CGWs into reality.
David Fajman et al 2024 Class. Quantum Grav. 41 233001
We review the status of mathematical research on the dynamical properties of relativistic fluids in cosmological spacetimes–both, in the presence of gravitational backreaction as well as the evolution on fixed cosmological backgrounds. We focus in particular on the phenomenon of fluid stabilization, which describes the taming effect of spacetime expansion on the fluid. While fluids are in general known to form shocks from regular initial data, spacetime expansion has been found to suppress this behaviour. During the last decade, various rigorous results on this problem have been put forward. We review these results, the mathematical methods involved and provide an outlook on open questions.
Keefe Mitman et al 2024 Class. Quantum Grav. 41 223001
Gravitational memory effects and the BMS freedoms exhibited at future null infinity have recently been resolved and utilized in numerical relativity simulations. With this, gravitational wave models and our understanding of the fundamental nature of general relativity have been vastly improved. In this paper, we review the history and intuition behind memory effects and BMS symmetries, how they manifest in gravitational waves, and how controlling the infinite number of BMS freedoms of numerical relativity simulations can crucially improve the waveform models that are used by gravitational wave detectors. We reiterate the fact that, with memory effects and BMS symmetries, not only can these next-generation numerical waveforms be used to observe never-before-seen physics, but they can also be used to test GR and learn new astrophysical information about our Universe.
Mila Bileska 2024 Class. Quantum Grav. 41 183001
This work re-derives and discusses non-Lorentz invariant variable speed of light (VSL) theories in the context of cosmological problems. Following a thorough introduction to the subject, an explicit solution demonstrating a possible dependence of the speed of light on the cosmological scale factor is presented and analyzed. The parameters of the initial ansatz,  , are constrained by requiring the VSL formulation to be a solution to the flatness and horizon problems. The theoretical section is concluded with a derivation of the change of entropy in a VSL Universe. Even though such findings imply that the speed of light can vary only in non-flat spacetime, an adapted approach using the Generalized Second Law of Thermodynamics is shown to loosen this restriction. Further, in the experimental section, recent evidence for a temporally varying fine structure constant at
, are constrained by requiring the VSL formulation to be a solution to the flatness and horizon problems. The theoretical section is concluded with a derivation of the change of entropy in a VSL Universe. Even though such findings imply that the speed of light can vary only in non-flat spacetime, an adapted approach using the Generalized Second Law of Thermodynamics is shown to loosen this restriction. Further, in the experimental section, recent evidence for a temporally varying fine structure constant at  significance is presented as a potential test for the VSL hypothesis. Overall, this work introduces and evaluates many aspects of non-Lorentz invariant VSL theories whilst encouraging future research and serving as a largely self-sufficient comprehensive overview paper.
significance is presented as a potential test for the VSL hypothesis. Overall, this work introduces and evaluates many aspects of non-Lorentz invariant VSL theories whilst encouraging future research and serving as a largely self-sufficient comprehensive overview paper.
Shalabi et al
We compute the leading order corrections to the expected value of the squared field amplitude of a massless real scalar quantum field due to curvature in a localized region of spacetime. We use Riemann normal coordinates to define localized field operators in a curved spacetime that are analogous to their flat space counterparts, and the Hadamard condition to find the leading order curvature corrections to the field correlations. We then apply our results to particle detector models, quantifying the effect of spacetime curvature in localized field probes.
Juarez-Aubry et al
We obtain semiclassical gravity solutions in the Poincaré fundamental domain of (3 + 1)-dimensional Anti-de Sitter spacetime, PAdS4, with a (massive or massless) Klein-Gordon field (with possibly non-trivial curvature coupling) with Dirichlet or Neumann boundary. Some results are explicitly and graphically presented for special values of the mass and curvature coupling (e.g. minimal or conformal coupling). In order to achieve this, we study in some generality how to perform the Hadamard renormalisation procedure for non-linear observables in maximally symmetric spacetimes in arbitrary dimensions, with emphasis on the stress-energy tensor. We show that, in this maximally symmetric setting, the Hadamard bi-distribution is invariant under the isometries of the spacetime, and can be seen as a 'single-argument' distribution depending only on the geodesic distance, which significantly simplifies the Hadamard recursion relations and renormalisation computations.
Tropper
We show that in supersymmetric theories, knowing the soft theorem for a single particle in a supermultiplet allows one to immediately determine soft theorems for the remainder of the supermultiplet. While soft theorems in supersymmetric theories have a rich history, they have only been chronicled for specific examples due to the fact that they are usually derived with technical Feynman diagrammatics or amplitudes methods. By contrast, we show that one can compute soft theorems non-perturbatively for entire supermultiplets in one line of algebra. This formalism is directly applicable to the most general supersymmetric theory: one with an arbitrary matter content, number of supercharges, and spacetime dimension. We give many explicit examples illustrating the scope and dexterity of this framework.
Lu
Supermassive binary black holes (SMBBHs) are natural products of the hierarchical mergers of galaxies with central black holes in the $\Lambda$ cold dark matter cosmogony. We briefly introduce the formation and evolution processes of SMBBHs 
{\bf and population synthesis modeling of SMBBHs across cosmic time. } Both the semi-analytical analysis and numerical simulations suggest that close SMBBHs are abundant in the universe, with rich electromagnetic signatures and enormous gravitational wave radiation. However, observational evidence for their existence is still uncertain. We summarize the current status of the electromagnetic searches and observations of these binaries, focusing on their morphological signatures, continuum spectra, line properties, and periodic variations modulated by their orbital motions. We review pulsar timing array observations of nanohertz gravitational waves from these SMBBHs, including from gravitational wave signals from
{\bf individual SMBBH sources and the stochastic background from the whole population of SMBBHs. }
Finally, we discuss the prospects of multimessenger studies for SMBBHs.
Soni et al
Progress in gravitational-wave astronomy depends upon having sensitive detectors with good data quality. Since the end of the LIGO-Virgo-KAGRA third Observing run in March 2020, detector-characterization efforts have lead to increased sensitivity of the detectors, swifter validation of gravitational-wave candidates and improved tools used for data-quality products. In this article, we discuss these efforts in detail and their impact on our ability to detect and study gravitational-waves. These include the multiple instrumental investigations that led to reduction in transient noise, along with the work to improve software tools used to examine the detectors data-quality. We end with a brief discussion on the role and requirements of detector characterization as the sensitivity of our detectors further improves in the future Observing runs.
Trending on Altmetric
Simon Langenscheidt and Daniele Oriti 2025 Class. Quantum Grav. 42 075010
We present a set of noncommuting tetrad-shift symmetries in 4D gravity in tetrad-connection variables, which allow expressing diffeomorphisms as composite transformations. Working on the phase space level for finite regions, we pay close attention to the corner piece of the generators, discuss various possible charge brackets, relative definitions of the charges, coupling to spinors and relations to other charges. What emerges is a picture of the symmetries and edge modes of gravity that bears local resemblance to a Poincare group  , but possesses structure functions. In particular, we argue that the symmetries and charges presented here are more amenable to discretisation, and sketch a strategy for this charge algebra, geared toward quantum gravity applications.
, but possesses structure functions. In particular, we argue that the symmetries and charges presented here are more amenable to discretisation, and sketch a strategy for this charge algebra, geared toward quantum gravity applications.
Ahmed Shalabi et al 2025 Class. Quantum Grav.
We compute the leading order corrections to the expected value of the squared field amplitude of a massless real scalar quantum field due to curvature in a localized region of spacetime. We use Riemann normal coordinates to define localized field operators in a curved spacetime that are analogous to their flat space counterparts, and the Hadamard condition to find the leading order curvature corrections to the field correlations. We then apply our results to particle detector models, quantifying the effect of spacetime curvature in localized field probes.
Benito A Juarez-Aubry and Milton C. Mamani-Leqque 2025 Class. Quantum Grav.
We obtain semiclassical gravity solutions in the Poincaré fundamental domain of (3 + 1)-dimensional Anti-de Sitter spacetime, PAdS4, with a (massive or massless) Klein-Gordon field (with possibly non-trivial curvature coupling) with Dirichlet or Neumann boundary. Some results are explicitly and graphically presented for special values of the mass and curvature coupling (e.g. minimal or conformal coupling). In order to achieve this, we study in some generality how to perform the Hadamard renormalisation procedure for non-linear observables in maximally symmetric spacetimes in arbitrary dimensions, with emphasis on the stress-energy tensor. We show that, in this maximally symmetric setting, the Hadamard bi-distribution is invariant under the isometries of the spacetime, and can be seen as a 'single-argument' distribution depending only on the geodesic distance, which significantly simplifies the Hadamard recursion relations and renormalisation computations.
Youjun Lu 2025 Class. Quantum Grav.
Supermassive binary black holes (SMBBHs) are natural products of the hierarchical mergers of galaxies with central black holes in the $\Lambda$ cold dark matter cosmogony. We briefly introduce the formation and evolution processes of SMBBHs 
{\bf and population synthesis modeling of SMBBHs across cosmic time. } Both the semi-analytical analysis and numerical simulations suggest that close SMBBHs are abundant in the universe, with rich electromagnetic signatures and enormous gravitational wave radiation. However, observational evidence for their existence is still uncertain. We summarize the current status of the electromagnetic searches and observations of these binaries, focusing on their morphological signatures, continuum spectra, line properties, and periodic variations modulated by their orbital motions. We review pulsar timing array observations of nanohertz gravitational waves from these SMBBHs, including from gravitational wave signals from
{\bf individual SMBBH sources and the stochastic background from the whole population of SMBBHs. }
Finally, we discuss the prospects of multimessenger studies for SMBBHs.
Jeremy G Baier et al 2025 Class. Quantum Grav. 42 075008
As pulsar timing arrays (PTAs) transition into the detection era of the stochastic gravitational wave background (GWB), it is important for PTA collaborations to review and possibly revise their observing campaigns. The detection of a 'single source' would be a boon for gravitational astrophysics, as such a source would emit gravitational waves for millions of years in the PTA frequency band. Here we present generic methods for studying the effects of various observational strategies, taking advantage of detector sensitivity curves, i.e. noise-averaged, frequency-domain detection statistics. The statistical basis for these methods is presented along with myriad examples of how to tune a detector towards single, deterministic signals or a stochastic background. We demonstrate that trading observations of the worst pulsars for high cadence campaigns on the best pulsars increases sensitivity to single sources at high frequencies while hedging losses in GWB and single source sensitivity at low frequencies. We also find that sky-targeted observing campaigns yield minimal sensitivity improvements compared with other PTA tuning options. Lastly, we show the importance of the uncorrelated half of the GWB, i.e. the pulsar-term, as an increasingly prominent sources of noise and show the impact of this emerging noise source on various PTA configurations.
Paul M Alsing 2025 Class. Quantum Grav.
We present a unitary phenomenological model for black hole evaporation based on the analogy of the laboratory process of spontaneous parametric down conversion (SPDC) \cite{Alsing:2015,Alsing:2016} when the black hole (pump) is allowed to deplete to zero mass. The model incorporates an additional new feature that allows for the interior Hawking partner-particles (idlers) behind the horizon to further generate new Hawking particle pairs of lower energy, one of which remains behind the horizon, and the other that adds to the externally emitted Hawking radiation (signals) outside the horizon. This model produces a Page curve for the evolution of the reduced density matrices for the evaporating black hole internal degrees of freedom entangled with the generated Hawking radiation pairs entangled across the horizon. The Page curve yields an entropy that rises at early times during the evaporation process as Hawking pairs are generated, reaches a peak midway through the evolution, and then decays to zero upon complete evaporation of the black hole. The entire system remains in a pure state at all times undergoing unitary (squeezed state) evolution, with the initial state of the black hole modeled as a bosonic Fock state of large, but finite number $n_{p0}$ of particles. For the final state of the system, the black hole reaches the vacuum state of zero mass, while the external Hawking radiation carries away the total energy of the initial black hole. Inside the horizon there remains $n_{p0}$ Hawking partner-particles of vanishingly small total energy, reminiscent of the "soft-hair" (zero energy) qubit model of Hotta, Nambu and Yamaguchi \cite{Hotta_Nambu_Yamaguchi:2018}, but now from a Hamiltonian for squeezed state generation perspective. The model presented here can be readily extended to encompass arbitrary initial pure states for the black hole, and in falling matter.
Javier Peraza and Martin Reiris 2025 Class. Quantum Grav.
We prove that some of the static Myers/Korotkin-Nicolai (MKN) vacuum 3+1 static black holes cannot be put into stationary rotation. Namely, they cannot be deformed into axisymmetric stationary vacuum black holes with non-zero angular momentum. Other than axisymmetry, no assumptions are made on the possible deformations. The phenomenon occurs in particular for those MKN solutions for which the distance along the axis between the two poles of the horizon is sufficiently small compared to the square root of its area. The MKN solutions, sometimes called periodic Schwarzschild, are physically regular but asymptotically Kasner.
The static rigidity presented here appears to be the first in the literature of General Relativity.
Carlos Barcelo et al 2025 Class. Quantum Grav.
No-hair theorems are uniqueness results constraining the form of the metric of black holes in general relativity. These theorems are typically formulated under idealized assumptions, involving a mixture of local (regularity of the horizon) and global aspects (vacuum spacetime and asymptotic flatness). This limits their applicability to astrophysical scenarios of interest such as binary black holes and accreting systems, as well as their extension to horizonless objects. A previous result due to Gürlebeck constrains the asymptotic multipolar structure of static spacetimes containing black holes surrounded by matter although not revealing the possible structure of the metric itself. In this work, we disentangle some of these assumptions in the static and axisymmetric case. Specifically: i) we show that only a one-parameter family of black-hole geometries is compatible with a given external gravitational field, ii) we also analyze the case in which the central object is close to forming an event horizon but is still horizonless and show that the deviations from the natural black-hole shape have to die off as one approaches the black hole limit under the physical principle that curvatures are bounded.
Isabella G Pretto et al 2025 Class. Quantum Grav. 42 075004
When numerically solving Einstein's equations for the evolution of binary black holes, physical imperfections in the initial data manifest as a transient, high-frequency pulse of 'junk radiation.' This unphysical signal must be removed before the waveform can be used. Improvements in the efficiency of numerical simulations now allow waveform catalogs containing thousands of waveforms to be produced. Thus, an automated procedure for identifying junk radiation is required. To this end, we present a new algorithm based on the empirical mode decomposition (EMD) from the Hilbert–Huang transform. This approach allows us to isolate and measure the high-frequency oscillations present in the measured irreducible masses of the black holes. The decay of these oscillations allows us to estimate the time from which the junk radiation can be ignored. To make this procedure more precise, we propose three distinct threshold criteria that specify how small the contribution of junk radiation has to be before it can be considered negligible. We apply this algorithm to 3403 BBH simulations from the Simulating eXtreme Spacetime catalog to find appropriate values for the thresholds in the three criteria. We find that this approach yields reliable decay time estimates, i.e. when to consider the simulation physical, for  98.5% of the simulations studied. This demonstrates the efficacy of the EMD as a suitable tool to automatically isolate and characterize junk radiation in the simulation of binary black hole systems.
98.5% of the simulations studied. This demonstrates the efficacy of the EMD as a suitable tool to automatically isolate and characterize junk radiation in the simulation of binary black hole systems.
Gabriel D'Andrade Furlanetto et al 2025 Class. Quantum Grav.
Fuzzy Dark Matter (FDM) is among the most suitable candidates to replace WIMPs and to resolve the puzzling mystery of dark matter. A galactic dark matter halo made of these ultralight bosonic particles leads to the formation of a solitonic core surrounded by quantum interference patterns that, on average, reproduce a Navarro-Frenk-White-like mass density profile in the outskirts of the halo. The structure of such a core is determined once the boson mass and the total mass of the halo are set. We investigated the capability of future astrometric Theia-like missions to detect the properties of such a halo within the FDM model, namely the boson mass and the core radius. To this aim, we built mock catalogs containing three-dimensional positions and velocities of stars within a target dwarf galaxy. We exploited these catalogs using a Markov Chain Monte Carlo algorithm and found that measuring the proper motion of at least 2000 stars within the target galaxy, with uncertainty $\sigma_v \leq 3$ km/s on the velocity components, will constrain the boson mass and the core radius with 3\% accuracy. Furthermore, the transition between the solitonic core and the outermost NFW-like density profile could be detected with an uncertainty of 7\%. Such results would not only help to confirm the existence of FDM, but they would also be useful for alleviating the current tension between galactic and cosmological estimations of the boson mass, or demonstrating the need for multiple particles with a broad mass spectrum as naturally arise String Axiverse.