ABSTRACT
We search for fast-expanding H i shells associated with Galactic supernova remnants (SNRs) in the longitude range ℓ ≈ 32° to 77° using 21 cm line data from the Inner-Galaxy Arecibo L-band Feed Array (I-GALFA) H i survey. Among the 39 known Galactic SNRs in this region, we find such H i shells in 4 SNRs: W44, G54.4–0.3, W51C, and CTB 80. All four were previously identified in low-resolution surveys, and three of those (excluding G54.4–0.3) were previously studied with the Arecibo telescope. A remarkable new result, however, is the detection of H i emission at both very high positive and negative velocities in W44 from the receding and approaching parts of the H i expanding shell, respectively. This is the first detection of both sides of an expanding shell associated with an SNR in H i 21 cm emission. The high-resolution I-GALFA survey data also reveal a prominent expanding H i shell with high circular symmetry associated with G54.4–0.3. We explore the physical characteristics of four SNRs and discuss what differentiates them from other SNRs in the survey area. We conclude that these four SNRs are likely the remnants of core-collapse supernovae interacting with a relatively dense (≳ 1 cm−3) ambient medium, and we discuss the visibility of SNRs in the H i 21 cm line.
Export citation and abstract BibTeX RIS
1. INTRODUCTION
The interstellar medium (ISM) is pervaded by small and large expanding neutral atomic shells (e.g., Heiles 1979, 1984; McClure-Griffiths et al. 2002; Ehlerová & Palouš 2005; McClure-Griffiths 2012). These H i shells are the interstellar material swept up by supersonic shock waves produced by mechanical energy sources, including H ii regions, stellar winds, supernova (SN) explosions, and infalling high-velocity (HV) clouds. The dominant and most violent sources are SNe, which dump huge amounts of kinetic energy into the Galactic ISM every 20–70 yr. However, it is not clear how this kinetic energy is conveyed to the diffuse ISM, because this depends on the types and the physical environments of SNe. Most SNe are core-collapse SNe (CCSNe) that have massive (⩾8 M☉) progenitors, and most CCSNe are produced in clusters (e.g., Higdon & Lingenfelter 2005). Most SN explosions, therefore, are correlated in both space and time, with such groupings frequently producing supershells and superbubbles with radii of more than a few hundred parsecs. Only Type Ia SNe and a small fraction of CCSNe are likely to occur in isolation. Single CCSNe probably explode inside a wind bubble created by their progenitor stars during the main-sequence phase. For stars of spectral type later than B0, this bubble size is small (≲ 1 pc), and the supernova remnants (SNRs) can interact with dense molecular clouds in their early evolution (Chevalier 1999). Type Ia's, on the other hand, probably explode in either warm diffuse environments of density n ∼ 0.1 cm−3 or in hot, rarefied gas with n ∼ 10−3 cm−3. The amount and characteristics of the kinetic energy imparted to the ISM by SNe should therefore be diverse, and their role in shaping the kinematics of the atomic phase of the ISM is not clear. Consequently, H i observations of shells and supershells are useful not only to understand the nature and origin of individual structures but also, with reasonably large statistical samples, to explore the overall effects of SNe on the ISM.
There have been a number of systematic searches for H i shells associated with individual Galactic SNRs. Koo & Heiles (1991, hereafter KH91) carried out a survey of Galactic SNRs in H i 21 cm line using the Hat-Creek 25 m telescope (FWHM =36'). They observed 103 northern Galactic SNRs and detected HV gas toward 15 SNRs including 3 SNRs known prior to the survey. Koo et al. (2004) searched for similar H i features toward 97 southern SNRs using the Parkes data from the Southern Galactic Plane Survey (FWHM =16'; McClure-Griffiths 2001) and identified another 10 SNRs. Since the SNRs are usually less than 1° in diameter, high-resolution observations are essential to confirm the association of HV H i features with the radio continuum SNR. Such confirmations have been made in several cases, e.g., CTB 80 (Koo et al. 1990), W44 (Koo & Heiles 1995), W51C (Koo & Moon 1997a), and IC 443 (Giovanelli & Haynes 1979; Braun & Strom 1986; Lee et al. 2008). There have also been studies of almost stationary H i shells or H i bubbles associated with SNRs, but it is generally difficult to derive the parameters of such low-velocity H i shells due to H i background confusion (e.g., Kothes et al. 2005; Cazzolato & Pineault 2005; see also references in Koo et al. 2004).
Recently, the 7 beam Arecibo L-band Feed Array (ALFA) receiver on the Arecibo 305 m telescope has enabled Galactic H i surveys of unprecedented breadth and sensitivity with a fully sampled 4' beam (Peek et al. 2010, 2011). The Inner Galaxy ALFA (I-GALFA) survey (Koo et al. 2010; Gibson et al. 2012) covers the portion of the first Galactic quadrant visible to Arecibo, an area of more than 1650 deg2 at longitudes of 32° to 77° in the Galactic plane and extending to 10° or more off the plane. I-GALFA uses 0.184 km s−1 velocity channels over an LSR velocity range of ∼ − 700 to +700 km s−1. Its brightness temperature rms noise is 0.2 K in single empty channels. This combination of high sensitivity, high spatial and spectral resolution, and large area and velocity coverage are well suited for a systematic study of H i shells and supershells in the diffuse ISM. In this first paper, we search for fast-expanding H i shells associated with known SNRs and consider the implications of our results on their nature. A forthcoming paper will discuss known H i shells and supershells as well as newly identified shells in the I-GALFA survey data. It is worth noting that the VLA Galactic Plane Survey (VGPS; Stil et al. 2006) and Canadian Galactic Plane Survey (CGPS; Taylor et al. 2003) cover most of the SNRs in the first quadrant in H i at higher spatial resolution (∼1'–2'). Their velocity coverage and sensitivity (±100–150 km s−1 and 1–3 K per 0.8 km s−1 channel) are not ideal to study faint, fast-expanding H i shells, but they can be useful to study shell fine structure at relatively low velocities.
In Section 2, we explain how we identify fast-expanding H i shells associated with SNRs and present the resulting list. In Section 3, we summarize the results on four SNRs that have associated fast-expanding H i shells. The two SNRs with new results, W44 and G54.4–0.3, are discussed in some detail. In Section 4, we explore the physical characteristics of the 4 SNRs and compare their properties to the other 35 SNRs in the survey area. Section 5 summarizes the paper.
2. IDENTIFICATION OF SNR H i SHELLS
There are 275 Galactic SNRs in Green's catalog (Green 2009a, 2009b). Among them, 39 SNRs are included in the I-GALFA area (Table 1). The SNR name, size, and type parameters in Table 1 are from Green (2009a). (See the table note for more parameter details.) Note that the 21 cm spectra of sources with high continuum brightness are noisy, so faint HV emission could not be seen in those objects. In Table 1, the ranks determined by KH91 are also listed. KH91 observed each SNR with the Hat Creek 85 foot telescope (FWHM = 36') at 9 points in a cross pattern centered on its catalog position and searched for SNRs with broad (≃ 10 km s−1) excess emission over the background. They divided SNRs into four ranks: 0, 1, 2, and 3, where rank 3 has the highest probability for an associated fast-expanding H i shell. In rank 1, the central excess emission is brighter than the four outermost positions; in rank 2, the central excess emission is brighter than all outer positions; in rank 3, there is also excess emission at the highest positive or negative velocities; and in rank 0, none of these criteria are met. Among 39 sources in Table 1, 26 were studied by KH91, who classified 9 of these as rank 3 SNRs. KH91 mapped the excess HV emission in these nine SNRs and concluded that the H i emission is not physically associated in 4 cases (marked as "(3)" in Table 1). Four SNRs are in rank 2. The other 13 (ranks 1 and 0) did not show any significant excess H i emission.
Table 1. Supernova Remnants in the I-GALFA Survey Area and Their Associated High-velocity H i Gases
| G-Name | Other Name | Size | Type | Tb, 21 cm | KH91 | Note on the High-velocity H i Gas from This Work |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| (arcmin) | (K) | Ranka | ||||
| G31.9 + 0.0 | 3C391 | 7 × 5 | S | 140 | 1 | ... |
| G32.1 − 0.9 | ... | 40? | C? | ... | ... | ... |
| G32.4 + 0.1 | ... | 6 | S | 1.7? | ... | ... |
| G32.8 − 0.1 | Kes 78 | 17 | S? | 8.6? | 2 | ... |
| G33.2 − 0.6 | ... | 18 | S | 2.2 | 0 | ... |
| G33.6 + 0.1 | Kes 79 | 10 | S | 45 | 2 | ... |
| G34.7 − 0.4 | W44 | 35 × 27 | C | 52 | 3 | Associated HV H i gas at +124 – +240 and −120 – −67 km s−1 |
| G35.6 − 0.4 | ... | 15 × 11 | S | 9.7 | ... | ... |
| G36.6 − 0.7 | ... | 25? | S? | ... | 0 | ... |
| G36.6 + 2.6 | ... | 17 × 13? | S | 0.6? | ... | ... |
| G39.2 − 0.3 | 3C396 | 8 × 6 | C | 74 | 2 | ... |
| G39.7 − 2.0 | W50 | 120 × 60 | ? | 2.2? | 3 | HV H i gas at +99 – +124 km s−1, but extends beyond the SNR |
| G40.5 − 0.5 | ... | 22 | S | 4.6 | (3) | HV H i gas at −124 – −70 km s−1, but portion of a larger structure |
| G41.1 − 0.3 | 3C397 | 4.5 × 2.5 | S | 401 | (3) | HV H i gas at +110 – +120 km s−1, but probably background emission |
| G42.8 + 0.6 | ... | 24 | S | 1.1? | (3) | HV H i gas at +100 – +108 km s−1, but probably background emission |
| G43.3 − 0.2 | W49B | 4 × 3 | S | 649 | 1 | ... |
| G43.9 + 1.6 | ... | 60? | S? | 0.5? | ... | ... |
| G45.7 − 0.4 | ... | 22 | S | 1.8? | 0 | ... |
| G46.8 − 0.3 | (HC30) | 17 × 13 | S | 13 | 1 | ... |
| G49.2 − 0.7 | W51C | 30 | S? | 39? | 3 | Associated HV H i gas at +91 – +160 km s−1 |
| G53.6 − 2.2 | 3C400.2 | 33 × 28 | S | 1.6 | 0 | ... |
| G54.1 + 0.3b | ... | 12.4 | C | 1.9 − 3.8 | 1 | ... |
| G54.4 − 0.3 | (HC40) | 40 | S | 3.6 | 3 | Associated HV H i gas at +80 – +130 km s−1 |
| G55.0 + 0.3 | ... | 20 × 15? | S | 0.3? | ... | ... |
| G55.7 + 3.4 | ... | 23 | S | 0.5 | 0 | ... |
| G57.2 + 0.8 | (4C21.53) | 12? | S? | 2.5? | 0 | ... |
| G59.5 + 0.1 | ... | 15 | S | 2.7? | ... | ... |
| G59.8 + 1.2 | ... | 20 × 16? | ? | 1.0 | ... | ... |
| G63.7 + 1.1 | ... | 8 | F | 6.1 | ... | ... |
| G65.1 + 0.6 | ... | 90 × 50 | S | 0.2 | ... | ... |
| G65.3 + 5.7 | ... | 310 × 240 | S? | 0.1? | (3) | HV H i gas at −122 – −159 km s−1, but no morphological relation |
| G65.7 + 1.2 | DA 495 | 22 | F | 2.1 | 2 | ... |
| G67.7 + 1.8 | ... | 15 × 12 | S | 1.1 | ... | ... |
| G68.6 − 1.2 | ... | 23 | ? | 0.3? | ... | ... |
| G69.0 + 2.7 | CTB 80 | 80? | ? | 3.8? | 3 | Associated HV H i gas at +43 – +110 km s−1 |
| G69.7 + 1.0 | ... | 16 × 14 | S | 1.7 | ... | ... |
| G73.9 + 0.9 | ... | 27 | S? | 2.7 | 0 | ... |
| G74.0 − 8.5 | Cygnus Loop | 230 × 160 | S | 1.2 | 0 | ... |
| G74.9 + 1.2 | CTB 87 | 8 × 6 | F | 38 | 0 | ... |
Notes. (1) The size is the angular diameter in radio continuum; a single value is quoted for nearly circular remnants, and the product of two values, the major and minor axes, is quoted for elongated remnants. (2) The type codes "S," "F," or "C" represent SNRs with a "shell," "filled-center," or "composite" radio structure. Uncertain parameters are listed with a question mark. (3) The mean brightness temperature at 21 cm Tb, 21 cm is calculated from the 1 GHz flux (F1 GHz) and spectral index α (Fν∝να) in Green's catalog, i.e., Tb = 1.42αF1 GHzλ2/(2kΔΩS) where λ is 21.1 cm and ΔΩS is the solid angle of the source in steradians. For sources without spectral indexes, we adopt −0.5. We use the area of a circle (or ellipse) corresponding to the sizes in Table 1 as the solid angle.
aRank "(3)" SNRs were classified as "3" but regarded to be not-associated with the SNRs by KH91.
bThis SNR is classified as type "C" since a larger radio shell at 1.4 GHz is detected by Lang et al. (2010). Its size and surface brightness, which is 100–200 mJy beam−1 with a beam of 6 82 × 6
82 × 6 60, are used to calculate Tb.
60, are used to calculate Tb.
Download table as: ASCIITypeset image
In order to identify fast-expanding shells associated with SNRs, we examined whether enhanced emission is present at the SNR position at high positive/negative velocities in several ways. We first inspected average, background-subtracted H i spectra toward individual SNRs as KH91 did. The average spectrum was obtained from a circular area with 1.1 times the SNR radius, while the background spectrum was obtained from an annular ring of 3' thickness surrounding the SNR. The radial interval between the SNR circle and the background ring was either 9' or 0.5 times the SNR radius, whichever was smaller. If another bright radio continuum source was located near the SNR, we left an appropriate space between the SNR circle and the background ring. We confirmed that all SNRs classified as rank 3 by KH91 show excess emission at high positive/negative velocities in their background-subtracted spectra, but we could not find additional SNRs with such features.
The above approach could have missed associated H i emission limited to small areas. We therefore inspected individual channel maps as well as (ℓ, v) and (b, v) maps to search for HV H i emission features spatially correlated with the SNRs in radio continuum maps. These are mostly from the VGPS or CGPS 21 cm continuum data with ∼1' resolution. For SNRs outside these two survey areas, we used either the lower-resolution (∼4 3) Effelsberg 11 cm continuum data (Reich et al. 1990) or referred to previous works. Surprisingly, this detailed inspection yielded no additional detections. Instead, we confirmed the conclusion of KH91 that the HV emission in four rank 3 SNRs extended beyond the spatial extent of SNRs, so that it was probably not associated with the SNRs (marked as "(3)" in Table 1). In one of them (G40.5–0.5), we found that the HV H i emission is part of a much larger and prominent expanding shell. This result will be discussed in a forthcoming paper.
3) Effelsberg 11 cm continuum data (Reich et al. 1990) or referred to previous works. Surprisingly, this detailed inspection yielded no additional detections. Instead, we confirmed the conclusion of KH91 that the HV emission in four rank 3 SNRs extended beyond the spatial extent of SNRs, so that it was probably not associated with the SNRs (marked as "(3)" in Table 1). In one of them (G40.5–0.5), we found that the HV H i emission is part of a much larger and prominent expanding shell. This result will be discussed in a forthcoming paper.
We are therefore left with the five rank 3 SNRs of KH91, but we suspect the HV H i emission in W50 (G39.7–2.0) is probably not associated with the SNR. W50 is a large, elongated shell-like SNR with SS 433 at the center, and KH91 reported the presence of very weak, extended H i emission at high positive velocities along the northern edge of the SNR where the continuum emission is enhanced (cf. Lockman et al. 2007). The high-resolution I-GALFA data confirm the presence of weak, filamentary H i emission along the SNR edge that appears to be connected to other H i structures well outside the SNR. We therefore regard the spatial correlation between the H i emission and the SNR as a coincidence. Our results are summarized in the last column of Table 1, where we comment only on the HV emission features. We do see some low-velocity H i features that may be associated with SNRs, but many of these are confusing, and the scope of the present paper is limited to fast-expanding H i shells in SNRs.
3. SUPERNOVA REMNANTS WITH FAST-EXPANDING H i SHELLS
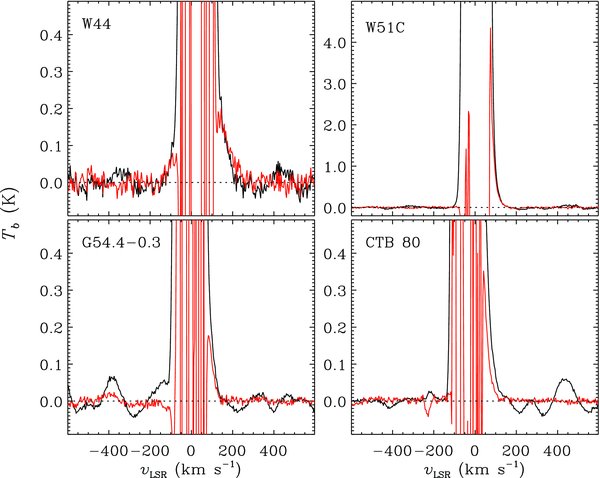
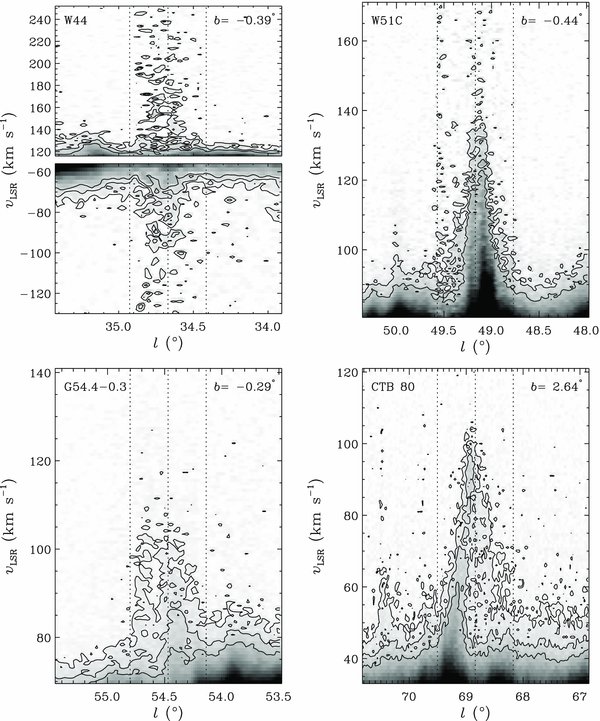
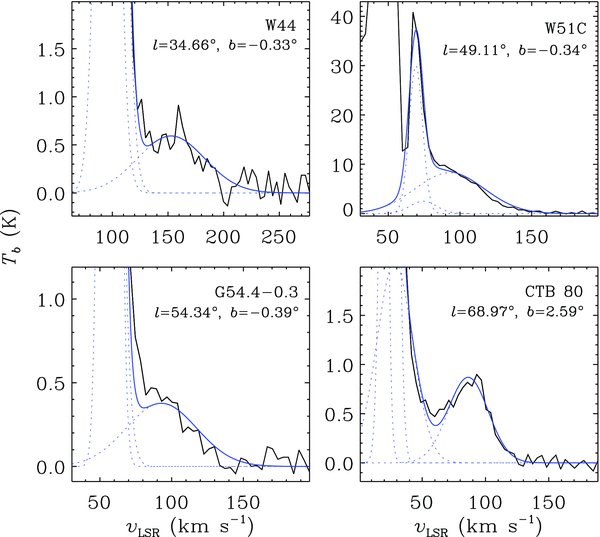
We have identified four SNRs that have associated HV H i gas: G34.7–0.4 (W44), G49.2–0.7 (W51C), G54.4–0.3 (HC40), and G69.0 + 2.7 (CTB 80). All four were ranked 3 by KH91, and follow-up high resolution observations have been made for SNRs W44, W51C, and CTB 80 (Koo & Heiles 1995; Koo & Moon 1997a; Koo et al. 1993). Figure 1 shows their average H i line profiles while Figure 2 shows (ℓ, v) maps across the centers of these four SNRs. (See Figure 3 for the areas used to derive these profiles.) The average profiles show some fluctuations in baseline, but they are removed in background-subtracted profiles. Figures 1 and 2 show that these four SNRs have excess H i emission at highest positive velocities. In W44, a faint, but clear, excess emission at highest negative velocities is also visible. Integrated (ℓ, b) maps in Figure 3 show the spatial distribution of HV H i emissions. The overlaid radio contours of SNRs clearly show that the HV H i gas is confined inside the SNR boundaries of W44 and G54.4–0.3. We discuss W44 and G54.4–0.3 in some detail below, where new results are obtained. We also briefly comment on the other two SNRs, W51C and CTB 80, where the I-GALFA results agree with previous findings.
Figure 1. Average H i 21 cm line profiles of SNRs that have associated high-velocity H i emission. Average profiles toward the SNRs are in black, while background-subtracted profiles are in red. (See Section 2 for details of the background subtraction.) Variations in H i 21 cm brightnesses between the source and background directions cause the wild fluctuations in the background-subtracted profiles at low velocities (|vLSR| ≲ 100 km s−1), but these have no effect on our analysis.
Download figure:
Standard image High-resolution imageFigure 2. I-GALFA (ℓ, v) maps of H i emission of four SNRs. Each longitude–velocity map is at the latitude given in its upper-right corner. The central longitude of the SNR is marked by the middle dotted line in each panel. The other two dotted lines indicate the boundary of the SNR. The gray scale varies from 0 to 5 K (white to black). Contours are 0.5 and 1.0 K for W51C and 0.3, 0.6, and 1.0 K for the other SNRs.
Download figure:
Standard image High-resolution imageFigure 3. H i maps of the fast-expanding H i shells in four SNRs. The lower right corner of each panel gives the SNR name and velocity range for integration in km s−1. For W44, both positive- and negative-velocity H i emissions have been used, although the former dominates. The scale bar units are K km s−1. Red contours show the SNR morphology in 21 cm radio continuum, from the CGPS for CTB 80 and the VGPS for the others. Contour levels are written at the upper left corner of each panel in kelvins. The black solid circle in each plot shows the mean size of the SNR in radio continuum. Two dotted circles mark the annulus used for estimating the background emission in deriving the average profiles in Figure 1. The size of W51C is 48', and other sizes are from Green's catalog. To aid comparison to literature studies in Equatorial coordinates, arrows are shown in each frame indicating right ascension and declination (J2000) coordinate directions.
Download figure:
Standard image High-resolution image3.1. W44 (G34.7–0.4)
3.1.1. Previous Studies
W44 is a middle aged SNR (∼2× 104 yr) of mixed morphology, being shell-type in radio continuum but center-filled in X-rays (Rho & Petre 1998). The radio continuum shell is somewhat elongated (35' × 27'), and the southeastern13 portion of the SNR shows enhanced radio emission (Figure 3; see also Castelletti et al. 2007). The pulsar PSR 1853+01 with a spin-down age of ∼2× 104 yr lies 9' southwest of the center of W44, embedded in an X-ray emitting pulsar wind nebula (PWN; Petre et al. 2002; Wolszczan et al. 1991). H i gas at very high positive velocities (≳ + 130 km s−1) accelerated by the SNR shock has been detected inside the remnant and studied using the Arecibo telescope (Koo & Heiles 1995). Ample evidence indicates the SNR is interacting with a molecular cloud in the southeast at vLSR = +46.6 km s−1 (Seta et al. 1998; Reach et al. 2005 and references therein). An extensive, organized system of thin and knotty H2 filaments filling the SNR may indicate that the SN exploded inside a molecular cloud (Reach et al. 2005; Froebrich et al. 2011). Gamma-ray emission from the SNR has been detected by Fermi/LAT and AGILE/GRID at 50 MeV–10 GeV (Abdo et al. 2010; Giuliani et al. 2011). The emission is confined to an incomplete ring structure that matches well with the SNR but with a slight offset. The gamma-ray spectrum is well modeled with emission from cosmic-ray protons interacting with the nuclei in the ambient medium. Distance estimates to the SNR range from 2.6 to 3.2 kpc.
3.1.2. New Results
The I-GALFA images reveal several new H i features not seen in previous studies. First, we detect fast-moving H i gas associated with the SNR at both the highest positive and highest negative velocities. The negative-velocity emission is relatively faint, but clearly real (see below). The H i gas at positive and negative velocities must be from the receding and approaching hemispheres of the SNR, respectively. This is the first detection of both sides of an expanding SNR shell in the H i 21 cm emission line. We will discuss the visibility of fast-expanding H i shells in Section 4.2.
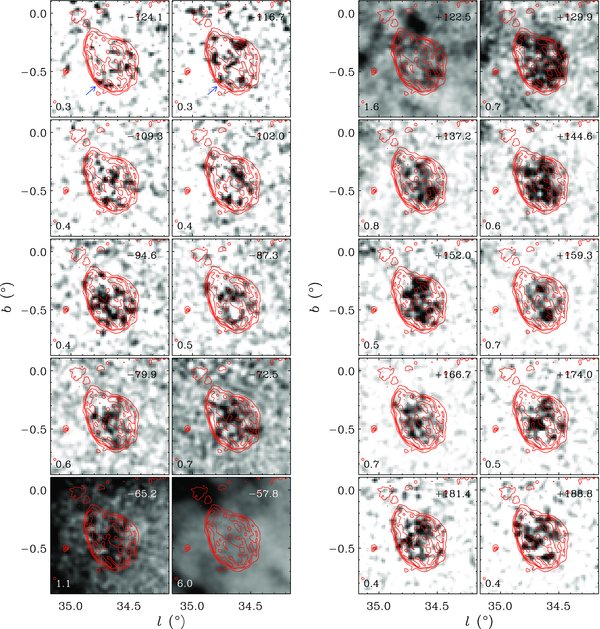
Figure 4 shows channel maps at both negative and positive velocities where we see H i emission confined inside the SNR boundary. At the highest negative velocities (−120 to −100 km s−1), a knotty, elongated emission feature is seen along the southeastern boundary of the SNR (blue arrow in first two panels). It is worth noting that this is where the SNR is currently interacting with the molecular cloud (see references in the previous paragraph). At velocities less negative than this, the emission in the central area has a ring-like shape. At positive velocities, the H i emission is more prominent. At the highest positive velocities, the H i gas is confined to the central area of the remnant with the ring-like morphology noted by Koo & Heiles (1995), and at vLSR = +130 km s−1, the H i gas forms a ring structure along the inner boundary of the SNR. This indicates that the H i gas is part of an expanding shell, and that the size of the H i shell is comparable to the radio continuum shell. This is in contrast to Koo & Heiles (1995), who concluded that the H i shell was smaller than the continuum shell from the extrapolation of the H i gas distribution at the highest velocities. Figure 4 indeed shows that the H i ring structure rather abruptly shifts from the central region to the SNR boundary as the velocity changes from +137 to +130 km s−1. We speculate that the total extent of the expanding H i shell is probably comparable to the radio continuum shell, but the shell is not complete.
Figure 4. Channel maps of HV H i gas associated with the SNR W44 at negative (left) and positive (right) velocities in the I-GALFA H i data. The central LSR velocity of each panel is written at the upper right corner in km s−1. The velocity width of one displayed channel is 3.68 km s−1; this is binned by a factor of 20 from the raw data and has a measured rms noise of 0.07 K. The H i brightness temperature in each gray scale ranges from 0 K (white) to the value (black) at the lower left corner of each panel in kelvins. Radio continuum emission at 21 cm is shown by red contours as in Figure 3. The blue arrows in the first two panels indicate an emission feature described in Section 3.1.2.
Download figure:
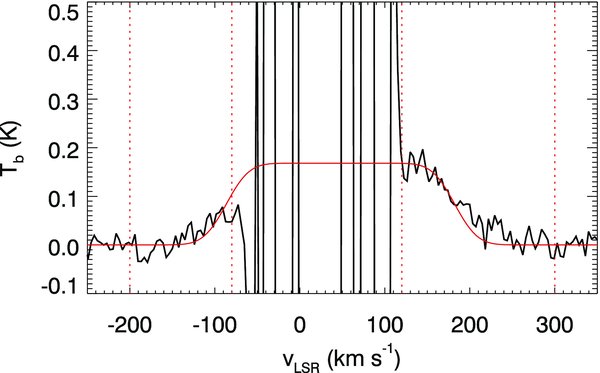
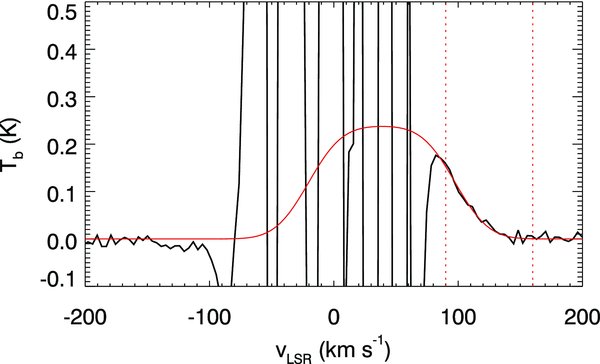
Standard image High-resolution imageFigure 5 shows the average H i profile of W44. If the H i shell is symmetric, we can in principle derive an accurate systemic velocity by measuring the velocity at which the line profile becomes symmetric. For example, if we naively fit a Gaussian to the line profile, we obtain a central velocity of +59 km s−1, which is considerably higher than the systemic velocity (+47 km s−1) of the associated molecular cloud. We attribute the discrepancy to the asymmetric mass distribution of the H i shell. The implied asymmetry also makes it difficult to derive an accurate mass. However, the uncertainty in the mass estimation is mainly due to the unobservable mass at low velocities, and, by fixing the central velocity, we can derive a reasonably accurate mass. The average line profile becomes flattened at velocities below +160 km s−1, i.e., it does not rise steeply as one might expect when the HV part (⩾160 km s−1) is the tail of a Gaussian profile, which is consistent with Koo & Heiles (1995). If the H i shell is uniform and expanding at a constant speed vexp, then the average H i 21 cm line profile would appear as a square profile that extends from −vexp to +vexp centered at the systemic velocity v0 (e.g., see Koo & Heiles 1991), i.e.,
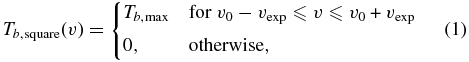
where Tb, max is the maximum brightness temperature, which is proportional to the total mass in the shell (see below). However, the shell probably does not coast at a constant speed, given non-uniformity/inhomogeneity of the ambient medium, turbulent motions produced by hydrodynamic instabilities, etc. We assume that the observed profile is composed of a flat profile convolved by a Gaussian profile, i.e.,
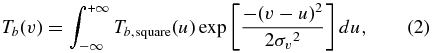
where σv is the dispersion of random velocities related to the velocity at FWHM ΔvFWHM by  .
.
Figure 5. Fit to the average background-subtracted H i profile of W44. Low-velocity residual brightness fluctuations are as in Figure 1. The red solid line is a best fit to the profile. The red dotted lines mark the velocity range where the fit has been performed. See Section 3.1.2 for an explanation of the fit.
Download figure:
Standard image High-resolution imageThe fast-moving gas is clumpy and has broad lines. In the SNR W51C, for example, Koo & Moon (1997a) resolved individual clumps using the Very Large Array (VLA) and found that their line profiles have FWHM of ∼40 km s−1. In the I-GALFA survey, we could not completely resolve out clumps from the background emission in velocity space, but we see many clumps that appear as prominent protrusions. Figure 6 shows some examples of HV bumps in the tails of strong background emission. We fit the HV parts of these spectra with several Gaussian components. Our purpose is only to obtain the widths of the HV bumps, so the fit parameters of the low-velocity components are unimportant. We obtain suitable results using four components for CTB 80 and three for the others (Figure 6), and we find ΔvFWHM ≈ 50 km s−1 for the HV components in all four SNRs. We adopt ΔvFWHM = 50 km s−1 as the characteristic value for the fit. The large velocity dispersion within the shell implies that the shell is dispersing, but its thickness will remain small compared to the radius of the shell until the very late stage of SNR evolution.
Figure 6. H i 21 cm spectra of some prominent HV clumps in individual SNRs (black lines). Their positions are given in the upper right corner of each panel. The HV parts of the spectra have been fitted by several Gaussian components, and the blue dotted and solid lines show the profiles of individual components and their sum, respectively. The components at the highest velocities are the ones related to the fast-expanding H i shells.
Download figure:
Standard image High-resolution imageWith the systemic velocity fixed at v0 ≡ +47 km s−1, we vary Tb, max and vexp. The fit was done using the IDL routine MPFIT (Markwardt 2009). The best fit profile is shown in Figure 5. Its parameters are vexp = 135 ± 2 km s−1 and Tb, max = 0.168 ± 0.005 K. The H i mass is derived from the average column density obtained from the fit, i.e.,  cm−2 considering both approaching and receding sides of the shell, by multiplying the area of W44. (Since the peak brightness temperature is only ∼0.2 K, we may assume that the H i emission is optically thin.) The derived H i mass is 393 ± 13 M☉, which implies a kinetic energy of 9.9 ± 0.4× 1049 erg. These numbers agree with those of Koo & Heiles (1995) within 10%–20%. The resulting dynamical age of the shell is t ≃ 0.3Rs/vs ≃ 2.7 × 104 yr (Cioffi et al. 1988), where we used a geometrical mean radius (12.5 pc at 2.8 kpc; see Tables 2 and 3 for the adopted distances to the SNRs) as the radius of the SNR, Rs. This dynamical age is somewhat larger than the characteristic spin-down age of the pulsar. Assuming that this mass was initially inside the volume of the SNR, i.e., inside a sphere of geometrical radius of 12.5 pc, the mean density of hydrogen nuclei in the ambient medium would be 1.9 ± 0.1 cm−3. The initial explosion energy, ESN, can be estimated from
cm−2 considering both approaching and receding sides of the shell, by multiplying the area of W44. (Since the peak brightness temperature is only ∼0.2 K, we may assume that the H i emission is optically thin.) The derived H i mass is 393 ± 13 M☉, which implies a kinetic energy of 9.9 ± 0.4× 1049 erg. These numbers agree with those of Koo & Heiles (1995) within 10%–20%. The resulting dynamical age of the shell is t ≃ 0.3Rs/vs ≃ 2.7 × 104 yr (Cioffi et al. 1988), where we used a geometrical mean radius (12.5 pc at 2.8 kpc; see Tables 2 and 3 for the adopted distances to the SNRs) as the radius of the SNR, Rs. This dynamical age is somewhat larger than the characteristic spin-down age of the pulsar. Assuming that this mass was initially inside the volume of the SNR, i.e., inside a sphere of geometrical radius of 12.5 pc, the mean density of hydrogen nuclei in the ambient medium would be 1.9 ± 0.1 cm−3. The initial explosion energy, ESN, can be estimated from
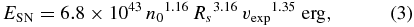
where n0 is the ambient density of hydrogen nuclei in cm−3, Rs is in pc, and vexp is in km s−1 (Cioffi et al. 1988). We assume solar metallicity. Substituting the derived values, i.e., n0 = 1.9 cm−3, Rs = 12.5 pc, and vexp = +135 km s−1, we have ESN = 3.2 ± 0.1 × 1050 erg. This is the energy required to heat and accelerate more or less uniformly distributed atomic gas. Since there is also fast-expanding (∼ + 30 km s−1), dense molecular gas accelerated by SN blast wave (Reach et al. 2005; Froebrich et al. 2011), some fraction of the total SN energy should have been used up for heating and accelerating the molecular gas. It would be interesting to derive the kinetic energy of shocked H2 filaments and compare it to that of the H i shell.
3.2. G54.4–0.3 (HC 40)
3.2.1. Previous Studies
G54.4–0.3 is a shell-type SNR of circular shape with a diameter of 40'. The shell is not complete, and its radio continuum brightness is not uniform (see the contour map in Figure 3; Junkes et al. 1992a). In the southeastern part of the remnant, the circular portion of the shell is missing, and instead faint continuum structures are visible connected to the tips of the bright ends. This probably indicates that the SNR blew out in this direction, presumably on encountering a rarefied medium there, and the shell was disrupted in the process. Junkes et al. (1992a) carried out CO observations and suggested an association with a molecular cloud at vLSR = + 36 to +44 km s−1. They proposed a distance of 3 kpc using the rotation curve of Burton (1988). Case & Bhattacharya (1998) adjusted this distance by adopting a revised rotation curve with R☉ = 8.5 kpc and Θ☉ = 220 km s−1 and obtained 3.3 kpc. If we use the rotation curves of Brand & Blitz (1993) or Levine et al. (2008), the near-side kinematic distance corresponding to the systemic velocity of +40 km s−1 in this direction is 3.9 and 3.1 kpc, respectively. We adopt the 3.3 kpc distance of Case & Bhattacharya (1998) in this paper. There are several H ii regions in this area at about the same distance, including the compact H ii region just outside the northwestern boundary of the remnant (Junkes et al. 1992b). Junkes (1996) observed the remnant with ROSAT and derived an absorbing hydrogen column density of 1× 1022 cm−2 and a plasma temperature of 2× 107 K. Boumis et al. (2005) detected optical emission lines in the northwestern edge of the shell and derived an absorbing hydrogen-nuclei column density of 2.9–4.0× 1022 cm−2. KH91 detected fast-moving H i gas at velocities +91–+108 km s−1.
3.2.2. New Results
This SNR has some of the most prominent H i shell structure in our sample. Figure 7 shows H i channel images of G54.4–0.3 at vLSR = + 53 to +108 km s−1. At the highest positive velocities, e.g., vLSR = + 100 km s−1, the H i gas is confined to the central area of the remnant, whereas at lower velocities, we see a well-defined ring structure as well as some emission filling the central area. This velocity structure indicates that the HV gas is the receding portion of an expanding shell. The shell has non-uniform brightness. A prominent feature is the bar-like structure extending from the center to the southwestern at vLSR = + 78 to +93 km s−1 (blue arrow in a panel at +89 km s−1). Its northeastern tip appears as a bright spot at (54 35, −0
35, −0 30) at vLSR = + 82–+89 km s−1. At low velocities, e.g., at vLSR = + 64–+78 km s−1, we see some correspondence between H i and radio continuum structures. First, the same southeastern portion of the H i shell is also weak and missing as in the continuum shell. Second, there is faint but enhanced H i emission coincident with the continuum shell at ⩾70 km s−1. Third, along the southwestern SNR shell, there is a larger filamentary H i structure just outside it at vLSR = + 64 to +78 km s−1. This external H i feature has the same curvature as the SNR shell, so it might be associated with the SNR too. Perhaps this is the boundary of the stellar wind bubble produced by the progenitor star, although it is not obvious how we can see the SNR shell inside a wind bubble.
30) at vLSR = + 82–+89 km s−1. At low velocities, e.g., at vLSR = + 64–+78 km s−1, we see some correspondence between H i and radio continuum structures. First, the same southeastern portion of the H i shell is also weak and missing as in the continuum shell. Second, there is faint but enhanced H i emission coincident with the continuum shell at ⩾70 km s−1. Third, along the southwestern SNR shell, there is a larger filamentary H i structure just outside it at vLSR = + 64 to +78 km s−1. This external H i feature has the same curvature as the SNR shell, so it might be associated with the SNR too. Perhaps this is the boundary of the stellar wind bubble produced by the progenitor star, although it is not obvious how we can see the SNR shell inside a wind bubble.
Figure 7. Channel maps of HV H i gas associated with the SNR G54.4–0.3 in the I-GALFA H i data. As in Figure 4, the central LSR velocity of each panel is shown in the upper left corner in km s−1, and the velocity width of one channel is 3.68 km s−1. The H i brightness temperature in each gray scale ranges from 0 K (white) to the value (black) at the lower left corner of each panel in kelvins. Radio continuum morphology of the SNR is shown by red contours as in Figure 3. The blue arrow in the +89.4 km s−1 panel marks an emission feature described in Section 3.2.2.
Download figure:
Standard image High-resolution imageWe derive the mass of the G54.4–0.3 H i shell in a similar fashion to W44, but using only positive velocities. We adopt ΔvFWHM = 50 km s−1 and assume a systemic velocity of +40 km s−1. The best-fit profile, shown in Figure 8, uses vexp = 59 ± 6 km s−1 and an H i mass of 580 ± 150 M☉ at 3.3 kpc. The corresponding kinetic energy is 2.8 ± 0.9× 1049 erg. The resulting dynamical age of the shell is t ≃ 0.3Rs/vs ≃ 9.5 × 104 yr, where we used Rs = 19.2 pc (20'). Again assuming that this mass was initially inside the volume of the SNR, the mean density of hydrogen nuclei in the ambient medium would be 0.79 ± 0.20 cm−3. With the above parameters, we obtain ESN = 1.5 ± 0.5 × 1050 erg. This is considerably smaller than the canonical value of 1× 1051 erg, but not unreasonable.
Figure 8. Fit to the average H i profile of G54.4–0.3. Low-velocity residual brightness fluctuations are as in Figure 1. The red solid line is a best fit to the profile. The red dotted lines mark the velocity range where the fit has been performed. See Section 3.1.2 for an explanation of the fit.
Download figure:
Standard image High-resolution imageTable 2. Physical Parameters of Supernova Remnants with Fast-expanding H i Shells
| Name | d | Rs | v0 | vexp | Age | H i Mass | K.E. | n0 | ESN | P?a | M?b |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| (kpc) | (pc) | (km s−1) | (km s−1) | (× 104 yr) | (M☉) | (× 1049 erg) | (cm−3) | (× 1050 erg) | |||
| W44 | 2.8 | 12.5 | 47 | 135(2) | 2.73(0.04) | 393(13) | 9.9(0.4) | 1.9(0.1) | 3.2(0.1) | y | y |
| W51Cc | 6 | 6 | 62 | 96(6) | 1.8(0.1) | >1200 | >17 | ∼100 | ∼19 | ... | y |
| G54.4–0.3 | 3.3 | 19.2 | 40 | 59(6) | 9.5(1.0) | 580(150) | 2.8(0.9) | 0.79(0.20) | 1.5(0.5) | ... | y |
| CTB 80d | 2 | 18.6 | 13 | 72(3) | 7.7(0.3) | 1050(210) | 7.6(1.5) | 1.5(0.3) | 3.8(0.9) | y | ... |
Notes. The distance (d), radius (Rs), and systemic velocity (v0) are adopted values, so that they do not have errors. The errors in W44 and G54.4–0.3 are formal errors from the fit. aDetection (y) of associated pulsars. References are Wolszczan et al. (1991) and Kulkarni et al. (1988) for W44 and CTB 80, respectively. bDetection (y) of associated molecular clouds. References are Wootten (1977), Koo & Moon (1997b), and Junkes et al. (1992a) for W44, W51C, and G54.4–0.3, respectively. cThe H i shell parameters are from Koo & Moon (1997a). W51C is interacting with a molecular cloud, and only a lower limit to the H i mass has been obtained. We adopt 100 cm−3 as a characteristic density of the cloud. dThe H i shell parameters are from Koo et al. (1990). Koo et al. (1990) obtained an H i mass of 1200 M☉ by fitting a Gaussian profile to the observed H i mass distribution. But an independent estimate of the mass of the shell is available from infrared studies (900 M☉; see Koo et al. 1990). We adopt the mean of the two as the mass of the expanding shell.
Download table as: ASCIITypeset image
Table 3. Distances to the SNRs in the I-GALFA Survey Area
| Coordinates | Distance | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| G-Name | ℓ | b | Type | Quoted | Σ − D | Radius | vdet, mina | Reference (s) |
| (°) | (°) | (kpc) | (kpc) | (pc) | (km s−1) | |||
| G31.9 + 0.0 | 31.89 | 0.03 | S | 8.5 | 5.4 | 7.3 | 59 | Green (2009a) |
| G32.1 − 0.9 | 32.12 | −0.90 | C? | 4.6 | ... | 26.8 | 72 | Folgheraiter et al. (1997) |
| G32.4 + 0.1 | 32.41 | 0.11 | S | 17 | 33.9 | 14.8 | 76 | Yamaguchi et al. (2004) |
| G32.8 − 0.1 | 32.81 | −0.06 | S? | ∼7.1 | 6.3 | 17.6 | 50 | Koralesky et al. (1998), Boumis et al. (2009) |
| G33.2 − 0.6 | 33.18 | −0.55 | S | ⋅⋅⋅ | 10.1 | 26.4 | 84 | ... |
| G33.6 + 0.1 | 33.70 | 0.01 | S | 7.8b | 5.1 | 11.3 | 53 | Frail & Clifton (1989), Green (2004, 2009a) |
| G34.7 − 0.4 | 34.67 | −0.39 | C | 2.8b | ... | 12.5 | 89 | Caswell et al. (1975), Green (2004, 2009a) |
| G35.6 − 0.4 | 35.59 | −0.50 | S | 3.7 | 7.6 | 6.9 | 76 | Green (2009b) |
| G36.6 − 0.7 | 36.59 | −0.69 | S? | ⋅⋅⋅ | ... | ... | 53 | ... |
| G36.6 + 2.6 | 36.58 | 2.60 | S | ⋅⋅⋅ | 20.5 | 44.3 | 52 | ... |
| G39.2 − 0.3 | 39.24 | −0.32 | C | 8.5 | ... | 8.6 | 64 | Lee et al. (2009) |
| G39.7 − 2.0 | 39.69 | −2.39 | ? | 6.0 | ... | 74.0 | 50 | Green (2009a) |
| G40.5 − 0.5 | 40.52 | −0.51 | S | 3.8c | 6.1 | 12.2 | 64 | Yang et al. (2006) |
| G41.1 − 0.3 | 41.11 | −0.31 | S | 10.6c | 6.1 | 5.2 | 94 | Jiang et al. (2010) |
| G42.8 + 0.6 | 42.82 | 0.64 | S | ∼6 | 10.3 | 20.9 | 50 | Marsden et al. (2001) |
| G43.3 − 0.2 | 43.27 | −0.19 | S | 10 | 4.8 | 5.0 | 87 | Green (2009a) |
| G43.9 + 1.6 | 43.91 | 1.61 | S? | ⋅⋅⋅ | 5.7 | 49.7 | 50 | ... |
| G45.7 − 0.4 | 45.69 | −0.39 | S | ⋅⋅⋅ | 9.1 | 29.1 | 76 | ... |
| G46.8 − 0.3 | 46.77 | −0.30 | S | ∼7.8 | 5.8 | 16.9 | 62 | Green (2009a) |
| G49.2 − 0.7 | 49.14 | −0.60 | S? | 6 | 1.9 | 26.2 | 51 | Koo et al. (1995) |
| G53.6 − 2.2 | 53.63 | −2.26 | S | 2.8 | 6.6 | 12.4 | 55 | Giacani et al. (1998), Green (2009a) |
| G54.1 + 0.3 | 54.09 | 0.26 | C | 6 | ... | 10.8 | 54 | Kim et al. (2013) |
| G54.4 − 0.3 | 54.47 | −0.29 | S | 3.3d | 3.7 | 19.2 | 52 | Junkes et al. (1992a), Case & Bhattacharya (1998) |
| G55.0 + 0.3 | 55.11 | 0.42 | S | 14 | 23.1 | 35.3 | 79 | Matthews et al. (1998), Green (2009a) |
| G55.7 + 3.4 | 55.60 | 3.51 | S | ⋅⋅⋅ | 14.3 | 47.8 | 76 | ... |
| G57.2 + 0.8 | 57.30 | 0.83 | S? | ⋅⋅⋅ | 14.3 | 25.0 | 74 | ... |
| G59.5 + 0.1 | 59.58 | 0.12 | S | ⋅⋅⋅ | 11.1 | 24.2 | 101 | ... |
| G59.8 + 1.2 | 59.81 | 1.20 | ? | ⋅⋅⋅ | 14.1 | 36.7 | 72 | ... |
| G63.7 + 1.1 | 63.79 | 1.17 | F | ⋅⋅⋅ | ... | ... | ... | ... |
| G65.1 + 0.6 | 65.27 | 0.30 | S | 9 | 6.8 | 87.8 | 93 | Green (2009a) |
| G65.3 + 5.7 | 65.18 | 5.66 | S? | 0.8 | 2.1 | 31.7 | 51 | Boumis et al. (2004), Green (2009a) |
| G65.7 + 1.2 | 65.72 | 1.21 | F | 1.5 | ... | 4.8 | 51 | Kothes et al. (2004), Green (2009a) |
| G67.7 + 1.8 | 67.74 | 1.82 | S | ∼12 | 18.0 | 23.4 | 79 | Mavromatakis et al. (2001) |
| G68.6 − 1.2 | 68.60 | −1.20 | ? | ⋅⋅⋅ | 19.2 | 64.2 | 50e | ... |
| G69.0 + 2.7 | 68.84 | 2.78 | ? | 2 | 1.8 | 23.3 | 50 | Koo et al. (1990) |
| G69.7 + 1.0 | 69.69 | 1.00 | S | 2f | 13.2 | 4.4 | 50 | Yoshita et al. (2000) |
| G73.9 + 0.9 | 73.91 | 0.88 | S? | ∼1.3 | 6.4 | 5.1 | 51 | Lozinskaya et al. (1993) |
| G74.0 − 8.5 | 73.98 | −8.56 | S | 0.44 | 1.2 | 12.3 | 53 | Green (2009a) |
| G74.9 + 1.2 | 74.94 | 1.14 | F | 6.1 | ... | 6.1 | 75 | Kothes et al. (2003), Green (2009a) |
Notes. Distance with a symbol of "∼" denotes that we adopt the average of possible distances given by reference(s). aMinimum expansion velocity for detection. bRecalculated by Green (2004) assuming a flat rotation curve with R☉ = 8.5 kpc and Θ☉ = 220 km s−1. cRecalculated by this work using the Galactic rotation curve of Brand & Blitz (1993) with R☉ = 8.5 kpc and Θ☉ = 220 km s−1. dRecalculated by Case & Bhattacharya (1998) assuming a flat rotation curve with R☉ = 8.5 kpc and Θ☉ = 220 km s−1. eThis remnant is outside the assumed disk radius of 15 kpc, so we simply adopt 50 km s−1 as the minimum velocity. fYoshita et al. (2000) suggested that G69.7 + 1.0 will be at a similar distance as CTB 80, since the column density of the ISM between us and G69.7 + 1.0 is analogous with that of CTB 80. In this paper, we adopt 2 kpc for both CTB 80 and G69.7 + 1.0.
Download table as: ASCIITypeset image
3.2.3. Others
G49–0.7 (W51C) is a middle aged, shell-type SNR interacting with a molecular cloud. Koo & Moon (1997a, 1997b) obtained high-resolution H i and CO observations and developed a model in which the fast-moving H i gas is produced by the SNR shock propagating into a molecular cloud. The SNR is one of the most luminous γ-ray sources in the Galaxy (Abdo et al. 2009). The I-GALFA results for the HV H i gas in Figures 1–3 agree with previous results.
G69.0 + 2.7 (CTB 80) is one of the first infrared SNRs detected by IRAS (Fesen et al. 1988). It appears as a large (∼1°), spherical shell-type SNR in IR while, in radio continuum, only the northern portion of the shell is bright due to the interaction with the pulsar. Koo et al. (1990, 1993) carried out H i studies using the Arecibo telescope and the VLA and confirmed the large size of the SNR shell and its old age (∼1× 105 yr). Again, the I-GALFA HV H i results in Figures 1–3 agree with previous results.
4. DISCUSSION
4.1. Properties of H i SNRs
We have detected four SNRs with fast expanding H i shells in the I-GALFA survey area. Table 2 summarizes their parameters: distance d, radius Rs, systemic velocity v0, expansion speed vexp, dynamical age, H i mass, kinetic energy, ambient density n0, and initial explosion energy ESN. The table also lists whether the remnant has an associated pulsar and whether it is interacting with a molecular cloud. The parameters of W44 and G54.4–0.3 are those derived in this work, whereas those of W51C and CTB 80 are from previous studies.
There are several points to make. First, all four SNRs are middle aged (1.8–9.5× 104 yr). Second, the ambient densities are ≳ 1 cm−3, considerably larger than the densities of either the warm or hot diffuse ISM filling most of the interstellar volume. In particular, three SNRs are interacting with molecular clouds. Third, two SNRs are the remnants of CCSNe with associated PWNe. The other two remnants, G54.4–0.3 and W51C, do not have associated PWNe, but their interactions with molecular clouds suggests they also likely have massive progenitors. In summary, the SNRs with H i shells (hereafter H i SNRs) that are detected are middle-aged SNRs of probable CCSN origin interacting with a relatively dense medium.
The dynamical evolution of middle aged SNRs in a uniform medium was studied in detail by Cioffi et al. (1988), who derived analytic expressions for radius Rs and expansion velocity vs that describe the results of their one-dimensional numerical simulations. Koo & Kang (2004) proposed somewhat simpler but still accurate forms of the equations of Cioffi et al. (1988).14 We find it useful to introduce a parameter δ ≡ n0E51−0.861 where n0 is the density of hydrogen nuclei in the ambient medium divided by 1 cm−3, and E51 is the SN energy released to the ISM in units of 1051 erg. Note that δ is dimensionless. The advantage of introducing δ is that the radius and velocity of middle-aged SNRs are now related by
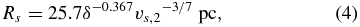
where vs, 2 ≡ (vs/100 km s−1). This equation is obtained by combining Equations (5)–(8) of Koo & Kang (2004). (Note that this is just another expression of Equation (3) except that their numerical coefficients differ by 2%.) In the (Rs, vs) plane, H i SNRs evolve along a line satisfying the above equation. In terms of δ, the expansion velocity of H i SNRs is given by (Equation (6) of Koo & Kang 2004)
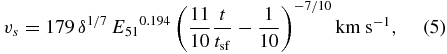
where the "shell formation time" tsf representing the onset of the formation of H i shell is defined by (Cioffi et al. 1988)
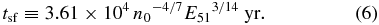
As pointed out by Koo & Kang (2004), the maximum disagreement between Equations (4)–(5) and the original Equations (3.22)–(3.23) of Cioffi et al. is less than 0.1% during t ∼ (1 − 13) tsf. The radius and velocity are now functions of δ, E51, and t/tsf instead of n0, E51, and t. Since the dependence of vs on E51 is weak, a single grid can be drawn in the (Rs, vs) plane to describe the evolution of H i SNRs in different physical environments.
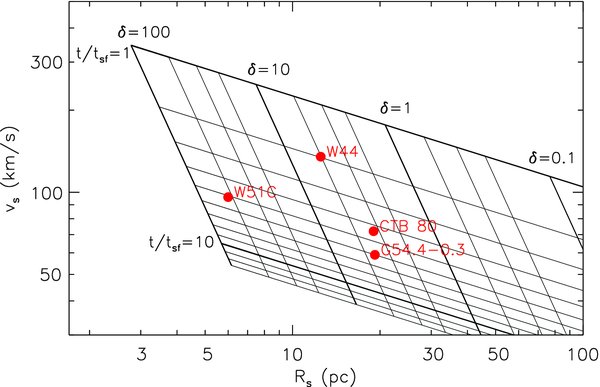
Figure 9 shows how the radius and velocity of H i SNRs evolve in time (t/tsf) for a given δ. The SNR develops a fast-expanding H i shell at t/tsf = 1, which expands and slows down along a line of constant δ as it evolves. For example, suppose an SNR has E51 = 1 in a uniform medium with n0 = 1, so that δ = 1. Then the SNR has an H i shell of (Rs, vs) = (20 pc, +179 km s−1) at t/tsf = 1 and (Rs, vs) = (40 pc, +34 km s−1) at t/tsf = 10, where tsf = 3.61 × 104 yr. The H i SNRs identified in the I-GALFA survey have radii of 6–19 pc and expansion velocities +59–+135 km s−1, or δ = 5–50 and t/tsf = 2–9. The expansion velocities of the detected H i shells are all greater than +50 km s−1, which is necessary to be clearly discernible from the Galactic background emission (see the next section). It is also worth noting that no large H i SNRs expected in the diffuse ISM have been detected, i.e., there are no H i SNRs where δ < 1 in Figure 9. This may be either because such SNRs are rare or because such SNRs are faint in radio continuum and "missed" in the current catalog of SNRs. We will discuss this further in next section.
Figure 9. Radius–velocity relation of H i SNRs. The grid is for E51 = 1. The grid shifts along lines of constant δ for different E51 but not much: e.g., for E51 = 0.1, the lines of constant t/tsf shift down by 36%. The thin grid lines in δ are drawn at 20, 30, and 50% of the thick-grid intervals, while those in t/tsf are at every 10%. The four H i SNRs identified in the I-GALFA survey are marked.
Download figure:
Standard image High-resolution image4.2. Visibility and Statistics of H i SNRs
The visibility or detectability of SNRs in the H i 21 cm line was investigated by Koo & Kang (2004). An important constraint on the visibility of H i SNRs is that they should be in the "right" positions in the Galaxy where the line-of-sight velocities of expanding H i shells can easily exceed the maximum or minimum LSR velocities of the Galactic background H i emission, e.g., along the loci of tangential points in the inner Galaxy. For example, W51C is in a high-visibility location, because its systemic velocity (+62 km s−1) is close to the maximum velocity (∼ + 90 km s−1; see Figure 2) of the background emission in this direction (ℓ = 49 2). In contrast, W44 is in a low-visibility location: its systemic velocity (+47 km s−1) is much less than the maximum velocity (+130 km s−1) in this direction (ℓ = 34
2). In contrast, W44 is in a low-visibility location: its systemic velocity (+47 km s−1) is much less than the maximum velocity (+130 km s−1) in this direction (ℓ = 34 7). Apparently, W44 is relatively young and has the largest expansion velocity, so that both its approaching and receding parts can be seen.
7). Apparently, W44 is relatively young and has the largest expansion velocity, so that both its approaching and receding parts can be seen.
The locations of the SNRs in the I-GALFA area are marked in Figure 10 (left), with filled circles for the four H i SNRs. Table 3 lists our adopted distances, where the fifth column gives the distances that are considered to be reliable. Twenty-eight SNRs have reliable distances, half of which are from the compilation by Green (2009a). The other half are from our own literature search, with references listed in the last column. The sixth column gives distances estimated using the surface brightness—diameter (Σ–D) relation (e.g., Case & Bhattacharya 1998; Arbutina et al. 2004; Guseinov et al. 2003). For this work, we adopt the Case & Bhattacharya (1998) version. The Σ–D relation has considerable dispersion, and its applicability has been criticized (e.g., Green 2004); without any other estimates, however, it still provides a useful reference. We use reliable distances wherever possible and Σ–D distances for other SNRs.
Figure 10. Left: distribution of vdet, min, the minimum expansion velocity of a fast-expanding SNR H i shell for detection. Areas with higher minimum expansion velocities are darker. The scale bar at the top displays velocity scales in a unit of km s−1. Contour levels are drawn at 70, 100, and 130 km s−1. The Sun is located at x = 0.0, y = 8.5 kpc. The dotted lines mark the boundaries of the I-GALFA survey at b = 0°, i.e., ℓ = 32° to 77°. The blue curved lines represent the four spiral arms of Taylor & Cordes (1993). The locations of the SNRs in the I-GALFA area are marked by red circles with diameters proportional to SNR size. The SNRs with fast-expanding H i shells are marked by the filled circles. Right: one-dimensional velocity profiles at ℓ = 32°. Minimum expansion velocities required for the detection of receding (top frame) and approaching (middle frame) portions of the shell are shown together with the systemic LSR velocity (vsys) as a function of distance from the Sun. vdet, min is the smaller of the two velocities (bottom frame). (See text for details.)
Download figure:
Standard image High-resolution imageThe background gray-scale map in Figure 10 (left) shows the minimum shell expansion velocity for detection, vdet, min. The Galactic disk is assumed to be axi-symmetric with radius 15 kpc and a flat rotation curve with R☉ = 8.5 kpc and Θ☉ = 220 km s−1. An expanding H i shell is considered to be visible if the LSR velocity of its receding endcap, which is the sum of the systemic LSR velocity and the expansion velocity, is greater than the maximum LSR velocities allowed by circular rotation in that direction by more than 50 km s−1or vice versa. This appears to be conservative considering that the turbulent velocity dispersion of the warm neutral medium is 27 km s−1 (Heiles & Troland 2003) and that the non-circular velocities due to spiral shocks are typically 20 km s−1 (e.g., Roberts 1969). However, note that the H i emission from fast-expanding SNR shells appears as very weak broad wings superposed on the Gaussian tails of background emission; in Figure 6, for example, the maximum LSR velocities in the directions of the four SNRs according to the flat rotation curve are, in the order of increasing Galactic longitude, +94, +54, +42, and +15 km s−1, respectively. H i shells along the tangent points in the inner Galaxy have small vdet, min (∼50 km s−1) because their positive-velocity wings can be easily detected. The H i shells near the outer boundary of the disk in the survey area also have small vdet, min, but, in this case, it is because their negative velocity wings can be easily detected. In order to help the understanding, Figure 10 (right) shows the variation of vdet, min for SNRs in the direction at ℓ = 32°. In the top and middle frames, the dotted line shows how the systemic LSR velocity (vsys) varies with distance from the Sun due to Galactic rotation. Note that the maximum and minimum systemic LSR velocities in this direction are 103 and −56 km s−1, respectively. This gives an approximate velocity range of the background H i emission. Therefore, for the receding portion of an expanding SNR shell to be detectable, its expansion velocity should be larger than (103 + 50) km s−1−vsys, where vsys is the systemic velocity of the shell (red line in the top frame). On the other hand, for the approaching portion to be detectable, which will appear as a negative-velocity wing, the expansion velocity should be larger than |(− 103–50) km s−1−vsys| (blue line in the middle frame). For just one part of the shell detectable, the required expansion velocity will be the smaller of the two (thick line in the bottom frame). Figure 10 shows that three SNRs (W51C, G54.4–0.3, CTB 80) are located where the vdet, min is relatively small, i.e., 50 km s−1, whereas W44 is located in a region where vdet, min ∼90 km s−1. Table 3 lists vdet, min at the position of each SNR.
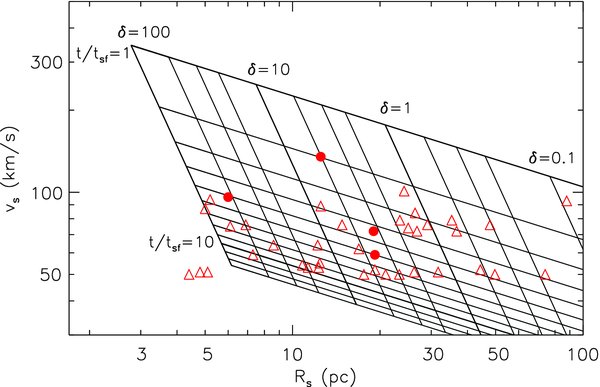
In Figure 10, there are many SNRs that are not detected in H i 21 cm line in spite of their favorable locations in areas where vdet, min is small. They could be either too young or too old to have an associated fast-expanding H i shell. Their nature can be inferred in Figure 11, which is same as Figure 9, but we now also mark the SNRs without detected H i shells using their minimum velocities for detection. In Figure 11, an SNR without detected H i can be either an old SNR with a velocity less than vdet, min or a young SNR above the grid, i.e., with velocity greater than that at t/tsf = 1. Note that if an SNR is above the grid, it means that the remnant is in adiabatic phase and does not have an H i shell. It is "too young," i.e., younger than tsf in Equation (6). Note that tsf is large when the ambient density is low. For small SNRs, e.g., those with Rs ⩽ 10–20 pc, the latter possibility is more likely unless they are in a dense environment, such as a molecular cloud. For larger SNRs, both possibilities are likely. Further observational studies will be helpful to address the nature of such SNRs individually.
Figure 11. Same as Figure 9 but with all SNRs not seen in I-GALFA H i also marked (empty triangles). The velocities of the latter SNRs are the minimum velocities of detection for their hypothetical H i shells. The four SNRs with detected fast-expanding H i shells (filled circles) are shown with their measured expansion velocities.
Download figure:
Standard image High-resolution imageAs a final comment, our study in this paper has targeted known SNRs, but there could be many missing SNRs. The estimated SN rate in our Galaxy ranges from 1.4 to 5.8 × 10−2 yr−1 (Li et al. 2011). If we adopt the recent estimate from the Lick Observatory Supernova Search, 2.84 ± 0.60 × 10−2 yr−1 (Li et al. 2011), the total number of radio SNRs in the Galaxy would be ∼2800, assuming 1 × 105 yr of visible radio continuum emission. Then, simply using the geometrical fraction of the survey area, which is 18% for a Galactic disk radius of 15 kpc, the expected number of radio SNRs in the survey area is ∼500. Therefore, the number of known SNRs (39) is only 8% of the expected population. This small fraction could be due to several factors: faintness of old SNRs in radio continuum, confusion due to Galactic background emission, collective explosions of CCSNe that produce supershells instead of SNRs, etc. (see Koo & Kang 2004; Higdon & Lingenfelter 2005; Brogan et al. 2006). So in principle, there could be many old SNRs or supershells not visible in radio continuum but visible in the H i 21 cm line, and it may be worthwhile to search for such H i features.
5. SUMMARY
The I-GALFA survey provides fully sampled H i data covering the Galactic plane between longitudes 32° to 77° and latitudes −10° to +10°. The high resolution (4') and high sensitivity (0.2 K) of the data provide an opportunity to investigate small-scale, faint H i emission in the diffuse ISM. In this paper, we have explored the I-GALFA data toward the all known 39 SNRs in order to search for associated fast-expanding H i shells. Our main results are as follows.
- 1.Among the 39 SNRs in the survey area, 4 SNRs show associated HV H i emission. These four SNRs were classified by KH91 as rank 3 SNRs with excess emission at the highest positive velocities in their low-resolution (30') H i study. KH91 listed another SNR (W50) as a candidate with associated HV H i emission out of 26 SNRs known in the survey area at that time. However, the high-resolution I-GALFA data show that the emission extends well beyond the SNR boundary, so we consider it not associated with the SNR. Surprisingly, we have not detected associated HV H i emission in any of the 10 SNRs discovered since the work of KH91.
- 2.The four SNRs where we have detected physically associated HV H i gas are G34.7–0.4 (W44), G49.2–0.7 (W51C), G54.4–0.3 (HC40), and G69.0 + 2.7 (CTB 80). Their velocity structures indicate that the HV H i gas is in portions of expanding shells. In the SNR W44, we see H i emission from both receding and approaching portions of the shell, which is the first ever such detection. In the other SNRs, we could see only the receding portions of the shells. The SNR G54.4–0.3 shows highly circularly symmetric H i emission that matches very well with its radio continuum morphology. There is a ring structure lying just outside the SNR boundary, which could be a pre-existing structure formed by the progenitor. We discuss the properties of the expanding H i shells in these two SNRs and derive their physical parameters. The other two SNRs have been studied previously in detail. The I-GALFA results are consistent with those previous studies.
- 3.The four SNRs with associated fast-expanding H i shells are all middle aged SNRs with ts = 1.8–9.5× 104 yr (Table 2). The expansion velocities of the shells range from 59 to 135 km s−1. Notably, their estimated ambient densities are all ≳ 1 cm−3, significantly higher than that of the warm or hot ISM filling most of interstellar space. Two of them have associated PWN, indicating that they are the remnants of CCSNe. The other two do not have PWN but are interacting with molecular clouds, so they are also likely the remnants of CCSNe. Therefore, the SNRs with H i shells (H i SNRs) that are detected are middle aged SNRs of probable CCSN origin interacting with a relatively dense medium. Large H i SNRs in the diffuse ISM could be detected in principle, but they have not found.
- 4.The visibility of H i SNRs depends on their location in the Galaxy. Three of the four detected H i SNRs (excluding W44) are located where the visibility is favorable. On the other hand, many SNRs are not detected in the H i 21 cm line despite having favorable locations. They could be either too young or too old to have an associated fast-expanding H i shell. We present a diagram (Figure 11) that can be used to infer the nature of these SNRs.
The Inner Galaxy ALFA (I-GALFA15) survey data are part of the Galactic ALFA (GALFA) H i project16 observed with the Arecibo L-band Feed Array (ALFA) on the 305 m William E. Gordon Telescope. The Arecibo Observatory is a U.S. National Science Foundation facility operated under sequential cooperative agreements with Cornell University and SRI International, the latter in alliance with the Ana G. Méndez-Universidad Metropolitana and the Universities Space Research Association. This work has been supported by the Korean Research Foundation under grant KRF-2008-313-C00372 to B.-C.K.
Footnotes
- 13
Directions in this paper are all in reference to Galactic coordinates, not J2000 Equatorial coordinates.
- 14
There was a typo in Equation (8) of Koo & Kang (2004): the index "−1/14" should be read as "1/14."
- 15
- 16